Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – December 20, 2014 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you understand the reasoning behind the answers. If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
Start from a situation where the external surplus is the equivalent of 2 per cent of GDP and the fiscal surplus is 2 per cent. If the fiscal balance stays constant and the external surplus rises to the equivalent of 4 per cent of GDP then you can conclude that National income also rises and the private surplus moves from 0 per cent of GDP to 2 per cent of GDP.
The answer is True.
The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero. The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (I – S) – positive if in deficit, negative if in surplus.
- The Budget Deficit (G – T) – negative if in surplus, positive if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
A simplification is to add (I – S) + (X – M) and call it the non-government sector. Then you get the basic result that the government balance equals exactly $-for-$ (absolutely or as a per cent of GDP) the non-government balance (the sum of the private domestic and external balances).
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
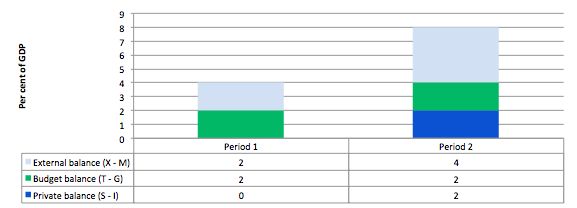
Consider the following graph and accompanying table which depicts two periods outlined in the question.
In Period 1, with an external surplus of 2 per cent of GDP and a fiscal surplus of 2 per cent of GDP the private domestic balance is zero. The demand injection from the external sector is exactly offset by the demand drain (the fiscal drag) coming from the fiscal balance and so the private sector can neither net save or spend more than they earn.
In Period 2, with the external sector adding more to demand now – surplus equal to 4 per cent of GDP and the fiscal balance unchanged (this is stylised – in the real world the fiscal balance will certainly change), there is a stimulus to spending and national income would rise.
The rising national income also provides the capacity for the private sector to save overall and so they can now save 2 per cent of GDP.
The fiscal drag is overwhelmed by the rising net exports.
This is a highly stylised example and you could tell a myriad of stories that would be different in description but none that could alter the basic point.
If the drain on spending (from the public sector) is more than offset by an external demand injection, then GDP rises and the private sector overall saving increases.
If the drain on spending from the fiscal balance outweighs the external injections into the spending stream then GDP falls (or growth is reduced) and the overall private balance would fall into deficit.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
- Back to basics – aggregate demand drives output
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
- Barnaby, better to walk before we run
- Saturday Quiz – June 19, 2010 – answers and discussion
Question 2:
Private sector wealth is invariant to the decision by government to issue bonds to the non-government sector to match its deficit spending as against not issuing any bonds.
The answer is True.
This answer relies on an understanding the banking operations that occur when governments spend and issue debt within a fiat monetary system. That understanding allows us to appreciate what would happen if a sovereign, currency-issuing government (with a flexible exchange rate) ran a fiscal deficit without issuing debt?
In this situation, like all government spending, the Treasury would credit the reserve accounts held by the commercial bank at the central bank. The commercial bank in question would be where the target of the spending had an account. So the commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a deposit would be made.
The transactions are clear: The commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a new deposit has been made. Further, the target of the fiscal initiative enjoys increased assets (bank deposit) and net worth (a liability/equity entry on their balance sheet). Taxation does the opposite and so a deficit (spending greater than taxation) means that reserves increase and private net worth increases.
This means that there are likely to be excess reserves in the “cash system” which then raises issues for the central bank about its liquidity management. The aim of the central bank is to “hit” a target interest rate and so it has to ensure that competitive forces in the interbank market do not compromise that target.
When there are excess reserves there is downward pressure on the overnight interest rate (as banks scurry to seek interest-earning opportunities), the central bank then has to sell government bonds to the banks to soak the excess up and maintain liquidity at a level consistent with the target. Some central banks offer a return on overnight reserves which reduces the need to sell debt as a liquidity management operation.
What would happen if there were bond sales? All that happens is that the banks reserves are reduced by the bond sales but this does not reduce the deposits created by the net spending. So net worth is not altered. What is changed is the composition of the asset portfolio held in the non-government sector.
The only difference between the Treasury “borrowing from the central bank” and issuing debt to the private sector is that the central bank has to use different operations to pursue its policy interest rate target. If it debt is not issued to match the deficit then it has to either pay interest on excess reserves (which most central banks are doing now anyway) or let the target rate fall to zero (the Japan solution).
There is no difference to the impact of the deficits on net worth in the non-government sector.
Mainstream economists would say that by draining the reserves, the central bank has reduced the ability of banks to lend which then, via the money multiplier, expands the money supply.
However, the reality is that:
- Building bank reserves does not increase the ability of the banks to lend.
- The money multiplier process so loved by the mainstream does not describe the way in which banks make loans.
- Inflation is caused by aggregate demand growing faster than real output capacity. The reserve position of the banks is not functionally related with that process.
So the banks are able to create as much credit as they can find credit-worthy customers to hold irrespective of the operations that accompany government net spending.
This doesn’t lead to the conclusion that deficits do not carry an inflation risk. All components of aggregate demand carry an inflation risk if they become excessive, which can only be defined in terms of the relation between spending and productive capacity.
It is totally fallacious to think that private placement of debt reduces the inflation risk. It does not.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
- Why history matters
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- The complacent students sit and listen to some of that
- Saturday Quiz – February 27, 2010 – answers and discussion
Question 3
When a government records a fiscal surplus which means it is withdrawing more purchasing power from the economy than it is adding, we know that it is seeking to attenuate the growth in aggregate demand.
The answer is that False.
The actual fiscal deficit outcome that is reported in the press and by Treasury departments is not a pure measure of the fiscal policy stance adopted by the government at any point in time. As a result, a straightforward interpretation of
Economists conceptualise the actual fiscal outcome as being the sum of two components: (a) a discretionary component – that is, the actual fiscal stance intended by the government; and (b) a cyclical component reflecting the sensitivity of certain fiscal items (tax revenue based on activity and welfare payments to name the most sensitive) to changes in the level of activity.
The former component is now called the “structural deficit” and the latter component is sometimes referred to as the automatic stabilisers.
The structural deficit thus conceptually reflects the chosen (discretionary) fiscal stance of the government independent of cyclical factors.
The cyclical factors refer to the automatic stabilisers which operate in a counter-cyclical fashion. When economic growth is strong, tax revenue improves given it is typically tied to income generation in some way. Further, most governments provide transfer payment relief to workers (unemployment benefits) and this decreases during growth.
In times of economic decline, the automatic stabilisers work in the opposite direction and push the fiscal balance towards deficit, into deficit, or into a larger deficit. These automatic movements in aggregate demand play an important counter-cyclical attenuating role. So when GDP is declining due to falling aggregate demand, the automatic stabilisers work to add demand (falling taxes and rising welfare payments). When GDP growth is rising, the automatic stabilisers start to pull demand back as the economy adjusts (rising taxes and falling welfare payments).
The problem is then how to determine whether the chosen discretionary fiscal stance is adding to demand (expansionary) or reducing demand (contractionary). It is a problem because a government could be run a contractionary policy by choice but the automatic stabilisers are so strong that the fiscal balance goes into deficit which might lead people to think the “government” is expanding the economy.
So just because the fiscal balance goes into deficit doesn’t allow us to conclude that the Government has suddenly become of an expansionary mind. In other words, the presence of automatic stabilisers make it hard to discern whether the fiscal policy stance (chosen by the government) is contractionary or expansionary at any particular point in time.
To overcome this ambiguity, economists decided to measure the automatic stabiliser impact against some benchmark or “full capacity” or potential level of output, so that we can decompose the fiscal balance into that component which is due to specific discretionary fiscal policy choices made by the government and that which arises because the cycle takes the economy away from the potential level of output.
As a result, economists devised what used to be called the Full Employment or High Employment Budget. In more recent times, this concept is now called the Structural Balance. As I have noted in previous blogs, the change in nomenclature here is very telling because it occurred over the period that neo-liberal governments began to abandon their commitments to maintaining full employment and instead decided to use unemployment as a policy tool to discipline inflation.
The Full Employment Budget Balance was a hypothetical construction of the fiscal balance that would be realised if the economy was operating at potential or full employment. In other words, calibrating the fiscal position (and the underlying fiscal parameters) against some fixed point (full capacity) eliminated the cyclical component – the swings in activity around full employment.
This framework allowed economists to decompose the actual fiscal balance into (in modern terminology) the structural (discretionary) and cyclical fiscal balances with these unseen fiscal components being adjusted to what they would be at the potential or full capacity level of output.
The difference between the actual fiscal outcome and the structural component is then considered to be the cyclical fiscal outcome and it arises because the economy is deviating from its potential.
So if the economy is operating below capacity then tax revenue would be below its potential level and welfare spending would be above. In other words, the fiscal balance would be smaller at potential output relative to its current value if the economy was operating below full capacity. The adjustments would work in reverse should the economy be operating above full capacity.
If the fiscal balance is in deficit when computed at the “full employment” or potential output level, then we call this a structural deficit and it means that the overall impact of discretionary fiscal policy is expansionary irrespective of what the actual fiscal outcome is presently. If it is in surplus, then we have a structural surplus and it means that the overall impact of discretionary fiscal policy is contractionary irrespective of what the actual fiscal outcome is presently.
So you could have a downturn which drives the fiscal balance into a deficit but the underlying structural position could be contractionary (that is, a surplus). And vice versa.
The question then relates to how the “potential” or benchmark level of output is to be measured. The calculation of the structural deficit spawned a bit of an industry among the profession raising lots of complex issues relating to adjustments for inflation, terms of trade effects, changes in interest rates and more.
Much of the debate centred on how to compute the unobserved full employment point in the economy. There were a plethora of methods used in the period of true full employment in the 1960s.
As the neo-liberal resurgence gained traction in the 1970s and beyond and governments abandoned their commitment to full employment , the concept of the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (the NAIRU) entered the debate – see my blogs – The dreaded NAIRU is still about and Redefing full employment … again!.
The NAIRU became a central plank in the front-line attack on the use of discretionary fiscal policy by governments. It was argued, erroneously, that full employment did not mean the state where there were enough jobs to satisfy the preferences of the available workforce. Instead full employment occurred when the unemployment rate was at the level where inflation was stable.
The estimated NAIRU (it is not observed) became the standard measure of full capacity utilisation. If the economy is running an unemployment equal to the estimated NAIRU then mainstream economists concluded that the economy is at full capacity. Of-course, they kept changing their estimates of the NAIRU which were in turn accompanied by huge standard errors. These error bands in the estimates meant their calculated NAIRUs might vary between 3 and 13 per cent in some studies which made the concept useless for policy purposes.
Typically, the NAIRU estimates are much higher than any acceptable level of full employment and therefore full capacity. The change of the the name from Full Employment Budget Balance to Structural Balance was to avoid the connotations of the past where full capacity arose when there were enough jobs for all those who wanted to work at the current wage levels.
Now you will only read about structural balances which are benchmarked using the NAIRU or some derivation of it – which is, in turn, estimated using very spurious models. This allows them to compute the tax and spending that would occur at this so-called full employment point. But it severely underestimates the tax revenue and overestimates the spending because typically the estimated NAIRU always exceeds a reasonable (non-neo-liberal) definition of full employment.
So the estimates of structural deficits provided by all the international agencies and treasuries etc all conclude that the structural balance is more in deficit (less in surplus) than it actually is – that is, bias the representation of fiscal expansion upwards.
As a result, they systematically understate the degree of discretionary contraction coming from fiscal policy.
The only qualification is if the NAIRU measurement actually represented full employment. Then this source of bias would disappear.
So a government could still be adopting an expansionary discretionary stance yet record a fiscal surplus because the automatic stabilisers are so strong.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
In q1, I don’t understand how you can conclude anything about the national income unless I am mistaken about what the definition of national income is. It is true that a net injection into the private domestic sector raises the national income but there are purely internal processes that could either raise or lower the GDP.
I agree with tonywn.
The correct answer is “true” only on various unstated assumptions.
On other assumptions the correct answer is is “false”.
The “explanation” suggested above is merely based on national accounting. While this is indeed important, it is only a set of logical implications derived from accounting definitions.
It is not a causal model of the economy which is required to predict effects on national income.
The suggested answer assumes that the increase in exports is not offset by declines in other expenditures. But investment, consumption or government expenditures could shift down.
Now it might be argued that autonomous expenditures other than exports are implicitly assumed to be constant because they are not mentioned – an implicit “ceteris paribus” assumption. To my mind this is a good argument, except that this blog often violates such an assumption. So an explicit “ceteris paribus” assumptions are required here, but these are lacking.
Moreover, there is a further complication because higher exports might appreciate the exchange rate. This would reduce the demand for import substitutes. The outcome on national income would then depend on a variety of supply and demand elasticities.
Question 2:
By issuing bonds, isn’t the government in effect injecting twice the financial assets into the private sector? Once with the paper that says “dollar” and once with the paper that says “bond”? I thought both were best though of as interchangeable. Both are liabilities backed by the faith of the US government.
KK to TW
I know it’s got a ring to it,but
Everything is captured in the GDP from the two perspectives,’Sources and Uses’. and also the suggested question states a continuous 2% fiscal surplus or drain to the private balance,over the periods.
Jon
No,bond sales by the treasury are a drain on liquidity and part of the Fed’s current monetary policy stance.where as,
The Dollar is spent by Gov/Treasury,accounted to as a deficit and in short,the stock of financial assets in the Private sector as deposits,($=$).
The Fed then adjusts the corresponding reserves and bonds,held by the commercial banks to the official target rate via the short term interest rate.They mainly achieve this by way of intervention in the federal funds market to ensure or maintain that the target rate of interest operates somewhere between the
discount rate and support rate.
p.s could you help explain this :-
http://english.pravda.ru/world/americas/19-12-2014/129343-cuba_usa_relations-0/