Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday quiz – June 9, 2012 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you understand the reasoning behind the answers. If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
Modern Monetary Theory teaches us that one of the dangers of public spending is that it can crowd out private spending.
The answer is True.
The question relates to the meaning of the term “crowding out”.
The normal presentation of the crowding out hypothesis which is a central plank in the mainstream economics attack on government fiscal intervention is more accurately called “financial crowding out”.
If I had have used the term “financial crowding” out then the answer would have been false.
At the heart of this conception of financial crowding out is the theory of loanable funds, which is a aggregate construction of the way financial markets are meant to work in mainstream macroeconomic thinking. The original conception was designed to explain how aggregate demand could never fall short of aggregate supply because interest rate adjustments would always bring investment and saving into equality.
In Mankiw, which is representative, we are taken back in time, to the theories that were prevalent before being destroyed by the intellectual advances provided in Keynes’ General Theory. Mankiw assumes that it is reasonable to represent the financial system as the “market for loanable funds” where “all savers go to this market to deposit their savings, and all borrowers go to this market to get their loans. In this market, there is one interest rate, which is both the return to saving and the cost of borrowing.”
This is back in the pre-Keynesian world of the loanable funds doctrine (first developed by Wicksell).
This doctrine was a central part of the so-called classical model where perfectly flexible prices delivered self-adjusting, market-clearing aggregate markets at all times. If consumption fell, then saving would rise and this would not lead to an oversupply of goods because investment (capital goods production) would rise in proportion with saving. So while the composition of output might change (workers would be shifted between the consumption goods sector to the capital goods sector), a full employment equilibrium was always maintained as long as price flexibility was not impeded. The interest rate became the vehicle to mediate saving and investment to ensure that there was never any gluts.
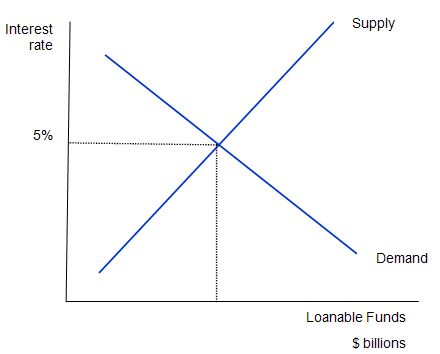
The following diagram shows the market for loanable funds. The current real interest rate that balances supply (saving) and demand (investment) is 5 per cent (the equilibrium rate). The supply of funds comes from those people who have some extra income they want to save and lend out. The demand for funds comes from households and firms who wish to borrow to invest (houses, factories, equipment etc). The interest rate is the price of the loan and the return on savings and thus the supply and demand curves (lines) take the shape they do.
Note that the entire analysis is in real terms with the real interest rate equal to the nominal rate minus the inflation rate. This is because inflation “erodes the value of money” which has different consequences for savers and investors.
Mankiw claims that this “market works much like other markets in the economy” and thus argues that (p. 551):
The adjustment of the interest rate to the equilibrium occurs for the usual reasons. If the interest rate were lower than the equilibrium level, the quantity of loanable funds supplied would be less than the quantity of loanable funds demanded. The resulting shortage … would encourage lenders to raise the interest rate they charge.
The converse then follows if the interest rate is above the equilibrium.
Mankiw also says that the “supply of loanable funds comes from national saving including both private saving and public saving.” Think about that for a moment. Clearly private saving is stockpiled in financial assets somewhere in the system – maybe it remains in bank deposits maybe not. But it can be drawn down at some future point for consumption purposes.
Mankiw thinks that budget surpluses are akin to this. They are not even remotely like private saving. They actually destroy liquidity in the non-government sector (by destroying net financial assets held by that sector). They squeeze the capacity of the non-government sector to spend and save. If there are no other behavioural changes in the economy to accompany the pursuit of budget surpluses, then as we will explain soon, income adjustments (as aggregate demand falls) wipe out non-government saving.
So this conception of a loanable funds market bears no relation to “any other market in the economy”.
Also reflect on the way the banking system operates – read Money multiplier and other myths if you are unsure. The idea that banks sit there waiting for savers and then once they have their savings as deposits they then lend to investors is not even remotely like the way the banking system works.
This framework is then used to analyse fiscal policy impacts and the alleged negative consquences of budget deficits – the so-called financial crowding out – is derived.
Mankiw says:
One of the most pressing policy issues … has been the government budget deficit … In recent years, the U.S. federal government has run large budget deficits, resulting in a rapidly growing government debt. As a result, much public debate has centred on the effect of these deficits both on the allocation of the economy’s scarce resources and on long-term economic growth.
So what would happen if there is a budget deficit. Mankiw asks: “which curve shifts when the budget deficit rises?”
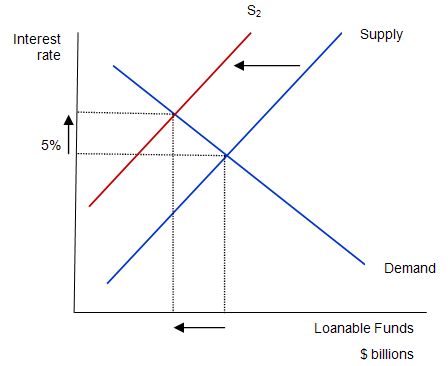
Consider the next diagram, which is used to answer this question. The mainstream paradigm argue that the supply curve shifts to S2. Why does that happen? The twisted logic is as follows: national saving is the source of loanable funds and is composed (allegedly) of the sum of private and public saving. A rising budget deficit reduces public saving and available national saving. The budget deficit doesn’t influence the demand for funds (allegedly) so that line remains unchanged.
The claimed impacts are: (a) “A budget deficit decreases the supply of loanable funds”; (b) “… which raises the interest rate”; (c) “… and reduces the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds”.
Mankiw says that:
The fall in investment because of the government borrowing is called crowding out …That is, when the government borrows to finance its budget deficit, it crowds out private borrowers who are trying to finance investment. Thus, the most basic lesson about budget deficits … When the government reduces national saving by running a budget deficit, the interest rate rises, and investment falls. Because investment is important for long-run economic growth, government budget deficits reduce the economy’s growth rate.
The analysis relies on layers of myths which have permeated the public space to become almost “self-evident truths”. Sometimes, this makes is hard to know where to start in debunking it. Obviously, national governments are not revenue-constrained so their borrowing is for other reasons – we have discussed this at length. This trilogy of blogs will help you understand this if you are new to my blog – Deficit spending 101 – Part 1 | Deficit spending 101 – Part 2 | Deficit spending 101 – Part 3.
But governments do borrow – for stupid ideological reasons and to facilitate central bank operations – so doesn’t this increase the claim on saving and reduce the “loanable funds” available for investors? Does the competition for saving push up the interest rates?
The answer to both questions is no! Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) does not claim that central bank interest rate hikes are not possible. There is also the possibility that rising interest rates reduce aggregate demand via the balance between expectations of future returns on investments and the cost of implementing the projects being changed by the rising interest rates.
MMT proposes that the demand impact of interest rate rises are unclear and may not even be negative depending on rather complex distributional factors. Remember that rising interest rates represent both a cost and a benefit depending on which side of the equation you are on. Interest rate changes also influence aggregate demand – if at all – in an indirect fashion whereas government spending injects spending immediately into the economy.
But having said that, the Classical claims about crowding out are not based on these mechanisms. In fact, they assume that savings are finite and the government spending is financially constrained which means it has to seek “funding” in order to progress their fiscal plans. The result competition for the “finite” saving pool drives interest rates up and damages private spending. This is what is taught under the heading “financial crowding out”.
A related theory which is taught under the banner of IS-LM theory (in macroeconomic textbooks) assumes that the central bank can exogenously set the money supply. Then the rising income from the deficit spending pushes up money demand and this squeezes interest rates up to clear the money market. This is the Bastard Keynesian approach to financial crowding out.
Neither theory is remotely correct and is not related to the fact that central banks push up interest rates up because they believe they should be fighting inflation and interest rate rises stifle aggregate demand.
However, other forms of crowding out are possible. In particular, MMT recognises the need to avoid or manage real crowding out which arises from there being insufficient real resources being available to satisfy all the nominal demands for such resources at any point in time.
In these situation, the competing demands will drive inflation pressures and ultimately demand contraction is required to resolve the conflict and to bring the nominal demand growth into line with the growth in real output capacity.
So, it is this context that the proposal in the question is True.
Further, while there is mounting hysteria about the problems the changing demographics will introduce to government budgets all the arguments presented are based upon spurious financial reasoning – that the government will not be able to afford to fund health programs (for example) and that taxes will have to rise to punitive levels to make provision possible but in doing so growth will be damaged.
However, MMT dismisses these “financial” arguments and instead emphasises the possibility of real problems – a lack of productivity growth; a lack of goods and services; environment impingements; etc.
Then the argument can be seen quite differently. The responses the mainstream are proposing (and introducing in some nations) which emphasise budget surpluses (as demonstrations of fiscal discipline) are shown by MMT to actually undermine the real capacity of the economy to address the actual future issues surrounding rising dependency ratios. So by cutting funding to education now or leaving people unemployed or underemployed now, governments reduce the future income generating potential and the likely provision of required goods and services in the future.
The idea of real crowding out also invokes and emphasis on political issues. If there is full capacity utilisation and the government wants to increase its share of full employment output then it has to crowd the private sector out in real terms to accomplish that. It can achieve this aim via tax policy (as an example). But ultimately this trade-off would be a political choice – rather than financial.
Question 2:
National accounting shows us that a government surplus equals a non-government deficit. But that doesn’t mean that if fiscal austerity ends up generating a budget surpluses that households and firms will be running deficits.
The answer is False.
The point is that the non-government sector is not equivalent to the private domestic sector in the sectoral balance framework. We have to include the impact of the external sector.
So this is a question about the sectoral balances – the government budget balance, the external balance and the private domestic balance – that have to always add to zero because they are derived as an accounting identity from the national accounts. The balances reflect the underlying economic behaviour in each sector which is interdependent – given this is a macroeconomic system we are considering.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero.
You can also write this as:
(S – I) + (T – G) = (X – M)
Which gives an easier interpretation (especially in relation to this question).
The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (S – I) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
- The Budget balance (T – G) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
Using this version of the sectoral balance framework:
(S – I) + (T – G) = (X – M)
So the domestic balance (left-hand side) – which is the sum of the private domestic sector and the government sector equals the external balance.
For the left-hand side of the equation to be positive (that is, in surplus overall) and the individual sectoral components to be in surplus overall, the right-hand side has to be positive (that is, an external surplus) and of sufficient magnitude.
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
The following graph and accompanying table shows a 8-period sequence where for the first four years the nation is running an external deficit (2 per cent of GDP) and for the last four year the external sector is in surplus (2 per cent of GDP).
For the question to be true we should never see the government surplus (T – G > 0) and the private domestic surplus (S – I > 0) simultaneously occurring – which in the terms of the graph will be the green and navy bars being above the zero line together.
You see that in the first four periods that never occurs which tells you that when there is an external deficit (X – M < 0) the private domestic and government sectors cannot simultaneously run surpluses, no matter how hard they might try. The income adjustments will always force one or both of the sectors into deficit.
The sum of the private domestic surplus and government surplus has to equal the external surplus. So that condition defines the situations when the private domestic sector and the government sector can simultaneously pay back debt.
It is only in Period 5 that we see the condition satisfied (see red circle).
That is because the private and government balances (both surpluses) exactly equal the external surplus.
So if the British government was able to pursue an austerity program with a burgeoning external sector then the private domestic sector would be able to save overall and reduce its debt levels. The reality is that this situation is not occuring.
Going back to the sequence, if the private domestic sector tried to push for higher saving overall (say in Period 6), national income would fall (because overall spending fell) and the government surplus would vanish as the automatic stabilisers responded with lower tax revenue and higher welfare payments.
Periods 7 and 8 show what happens when the private domestic sector runs deficits with an external surplus. The combination of the external surplus and the private domestic deficit adding to demand drives the automatic stabilisers to push the government budget into further surplus as economic activity is high. But this growth scenario is unsustainable because it implies an increasing level of indebtedness overall for the private domestic sector which has finite limits. Eventually, that sector will seek to stabilise its balance sheet (which means households and firms will start to save overall). That would reduce domestic income and the budget would move back into deficit (or a smaller surplus) depending on the size of the external surplus.
So what is the economics that underpin these different situations?
If the nation is running an external deficit it means that the contribution to aggregate demand from the external sector is negative – that is net drain of spending – dragging output down.
The external deficit also means that foreigners are increasing financial claims denominated in the local currency. Given that exports represent a real cost and imports a real benefit, the motivation for a nation running a net exports surplus (the exporting nation in this case) must be to accumulate financial claims (assets) denominated in the currency of the nation running the external deficit.
A fiscal surplus also means the government is spending less than it is “earning” and that puts a drag on aggregate demand and constrains the ability of the economy to grow.
In these circumstances, for income to be stable, the private domestic sector has to spend more than they earn.
You can see this by going back to the aggregate demand relations above. For those who like simple algebra we can manipulate the aggregate demand model to see this more clearly.
Y = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that the total national income (Y or GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
So if the G is spending less than it is “earning” and the external sector is adding less income (X) than it is absorbing spending (M), then the other spending components must be greater than total income.
Only when the government budget deficit supports aggregate demand at income levels which permit the private sector to save out of that income will the latter achieve its desired outcome. At this point, income and employment growth are maximised and private debt levels will be stable.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Barnaby, better to walk before we run
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
Question 3:
A hallmark of the neo-liberal period has been the declining share of wages in national income which in part meant that economic growth became more dependent on credit to maintain growth in consumption spending. However it is not necessary for real wages to grow in the coming years to reverse that trend. So real wage cuts under austerity programs could increase the wage share.
The answer is True.
A faster rate of real wages growth is not even a necessary condition much less a sufficient condition for a rising wage share.
Abstracting from the share of national income going to government, we can divide national income into the proportion going to workers (the “wage share”) and the proportion going to capital (the “profits share”). For the profit share to fall, the wage share has to rise (given the proportion going to government is relatively constant over time).
The wage share in nominal GDP is expressed as the total wage bill as a percentage of nominal GDP. Economists differentiate between nominal GDP ($GDP), which is total output produced at market prices and real GDP (GDP), which is the actual physical equivalent of the nominal GDP. We will come back to that distinction soon.
To compute the wage share we need to consider total labour costs in production and the flow of production ($GDP) each period.
Employment (L) is a stock and is measured in persons (averaged over some period like a month or a quarter or a year.
The wage bill is a flow and is the product of total employment (L) and the average wage (w) prevailing at any point in time. Stocks (L) become flows if it is multiplied by a flow variable (W). So the wage bill is the total labour costs in production per period.
So the wage bill = W.L
The wage share is just the total labour costs expressed as a proportion of $GDP – (W.L)/$GDP in nominal terms, usually expressed as a percentage. We can actually break this down further.
Labour productivity (LP) is the units of real GDP per person employed per period. Using the symbols already defined this can be written as:
LP = GDP/L
so it tells us what real output (GDP) each labour unit that is added to production produces on average.
We can also define another term that is regularly used in the media – the real wage – which is the purchasing power equivalent on the nominal wage that workers get paid each period. To compute the real wage we need to consider two variables: (a) the nominal wage (W) and the aggregate price level (P).
We might consider the aggregate price level to be measured by the consumer price index (CPI) although there are huge debates about that. But in a sense, this macroeconomic price level doesn’t exist but represents some abstract measure of the general movement in all prices in the economy.
Macroeconomics is hard to learn because it involves these abstract variables that are never observed – like the price level, like “the interest rate” etc. They are just stylisations of the general tendency of all the different prices and interest rates.
Now the nominal wage (W) – that is paid by employers to workers is determined in the labour market – by the contract of employment between the worker and the employer. The price level (P) is determined in the goods market – by the interaction of total supply of output and aggregate demand for that output although there are complex models of firm price setting that use cost-plus mark-up formulas with demand just determining volume sold. We shouldn’t get into those debates here.
The inflation rate is just the continuous growth in the price level (P). A once-off adjustment in the price level is not considered by economists to constitute inflation.
So the real wage (w) tells us what volume of real goods and services the nominal wage (W) will be able to command and is obviously influenced by the level of W and the price level. For a given W, the lower is P the greater the purchasing power of the nominal wage and so the higher is the real wage (w).
We write the real wage (w) as W/P. So if W = 10 and P = 1, then the real wage (w) = 10 meaning that the current wage will buy 10 units of real output. If P rose to 2 then w = 5, meaning the real wage was now cut by one-half.
So the proposition in the question – that nominal wages grow faster than inflation – tells us that the real wage is rising.
Nominal GDP ($GDP) can be written as P.GDP, where the P values the real physical output.
Now if you put of these concepts together you get an interesting framework. To help you follow the logic here are the terms developed and be careful not to confuse $GDP (nominal) with GDP (real):
- Wage share = (W.L)/$GDP
- Nominal GDP: $GDP = P.GDP
- Labour productivity: LP = GDP/L
- Real wage: w = W/P
By substituting the expression for Nominal GDP into the wage share measure we get:
Wage share = (W.L)/P.GDP
In this area of economics, we often look for alternative way to write this expression – it maintains the equivalence (that is, obeys all the rules of algebra) but presents the expression (in this case the wage share) in a different “view”.
So we can write as an equivalent:
Wage share – (W/P).(L/GDP)
Now if you note that (L/GDP) is the inverse (reciprocal) of the labour productivity term (GDP/L). We can use another rule of algebra (reversing the invert and multiply rule) to rewrite this expression again in a more interpretable fashion.
So an equivalent but more convenient measure of the wage share is:
Wage share = (W/P)/(GDP/L) – that is, the real wage (W/P) divided by labour productivity (GDP/L).
I won’t show this but I could also express this in growth terms such that if the growth in the real wage equals labour productivity growth the wage share is constant. The algebra is simple but we have done enough of that already.
That journey might have seemed difficult to non-economists (or those not well-versed in algebra) but it produces a very easy to understand formula for the wage share.
Two other points to note. The wage share is also equivalent to the real unit labour cost (RULC) measures that Treasuries and central banks use to describe trends in costs within the economy. Please read my blog – Saturday Quiz – May 15, 2010 – answers and discussion – for more discussion on this point.
Now it becomes obvious that if the nominal wage (W) grows faster than the price level (P) then the real wage is growing. But that doesn’t automatically lead to a growing wage share. So the blanket proposition stated in the question is false.
If the real wage is growing at the same rate as labour productivity, then both terms in the wage share ratio are equal and so the wage share is constant.
If the real wage is growing but labour productivity is growing faster, then the wage share will fall.
Only if the real wage is growing faster than labour productivity , will the wage share rise.
The wage share was constant for a long time during the Post Second World period and this constancy was so marked that Kaldor (the Cambridge economist) termed it one of the great “stylised” facts. So real wages grew in line with productivity growth which was the source of increasing living standards for workers.
The productivity growth provided the “room” in the distribution system for workers to enjoy a greater command over real production and thus higher living standards without threatening inflation.
Since the mid-1980s, the neo-liberal assault on workers’ rights (trade union attacks; deregulation; privatisation; persistently high unemployment) has seen this nexus between real wages and labour productivity growth broken. So while real wages have been stagnant or growing modestly, this growth has been dwarfed by labour productivity growth.
So the question is True because you have to consider labour productivity growth in addition to real wages growth before you can make conclusions about the movements in factor shares in national income.
It would be highly undesirable though to run a strategy that undermined productivity growth.
The following blog may be of further interest to you:
Question 4:
The payment of a positive interest return by the central bank on overnight bank reserves does not eliminate the need for it to conduct open market operations to ensure its policy rate is sustained (ignore any reserve requirements).
The answer is True.
This question tests your knowledge of central bank operations – in particular, its liquidity management operations that are used to maintain its target rate of interest in a modern monetary economy.
Mainstream macroeconomics textbooks tell students that monetary policy describes the processes by which the central bank determines “the total amount of money in existence or to alter that amount”. However, this is not what happens in the real world.
In Mankiw’s Principles of Economics (Chapter 27 First Edition) he say that the central bank has “two related jobs”. The first is to “regulate the banks and ensure the health of the financial system” and the second “and more important job”:
… is to control the quantity of money that is made available to the economy, called the money supply. Decisions by policymakers concerning the money supply constitute monetary policy (emphasis in original).
How does the mainstream see the central bank accomplishing this task? Mankiw says:
Fed’s primary tool is open-market operations – the purchase and sale of U.S government bonds … If the FOMC decides to increase the money supply, the Fed creates dollars and uses them buy government bonds from the public in the nation’s bond markets. After the purchase, these dollars are in the hands of the public. Thus an open market purchase of bonds by the Fed increases the money supply. Conversely, if the FOMC decides to decrease the money supply, the Fed sells government bonds from its portfolio to the public in the nation’s bond markets. After the sale, the dollars it receives for the bonds are out of the hands of the public. Thus an open market sale of bonds by the Fed decreases the money supply.
This description of the way the central bank interacts with the banking system and the wider economy is totally false. The reality is that monetary policy is focused on determining the value of a short-term interest rate. Central banks cannot control the money supply. To some extent these ideas were a residual of the commodity money systems where the central bank could clearly control the stock of gold, for example. But in a credit money system, this ability to control the stock of “money” is undermined by the demand for credit.
The theory of endogenous money is central to the horizontal analysis in Modern Monetary Theory (MMT). When we talk about endogenous money we are referring to the outcomes that are arrived at after market participants respond to their own market prospects and central bank policy settings and make decisions about the liquid assets they will hold (deposits) and new liquid assets they will seek (loans).
The essential idea is that the “money supply” in an “entrepreneurial economy” is demand-determined – as the demand for credit expands so does the money supply.
As credit is repaid the money supply shrinks. These flows are going on all the time and the stock measure we choose to call the money supply, say M3 (Currency plus bank current deposits of the private non-bank sector plus all other bank deposits from the private non-bank sector) is just an arbitrary reflection of the credit circuit.
So the supply of money is determined endogenously by the level of GDP, which means it is a dynamic (rather than a static) concept.
Central banks clearly do not determine the volume of deposits held each day. These arise from decisions by commercial banks to make loans. The central bank can determine the price of “money” by setting the interest rate on bank reserves. Further expanding the monetary base (bank reserves) as we have argued in recent blogs – Building bank reserves will not expand credit and Building bank reserves is not inflationary – does not lead to an expansion of credit.
With this background in mind, the question is specifically about the dynamics of bank reserves which are used to satisfy any imposed reserve requirements and facilitate the payments system. These dynamics have a direct bearing on monetary policy settings. Given that the dynamics of the reserves can undermine the desired monetary policy stance (as summarised by the policy interest rate setting), the central banks have to engage in liquidity management operations.
What are these liquidity management operations?
Well you first need to appreciate what reserve balances are.
The New York Federal Reserve Bank’s paper – Divorcing Money from Monetary Policy said that:
… reserve balances are used to make interbank payments; thus, they serve as the final form of settlement for a vast array of transactions. The quantity of reserves needed for payment purposes typically far exceeds the quantity consistent with the central bank’s desired interest rate. As a result, central banks must perform a balancing act, drastically increasing the supply of reserves during the day for payment purposes through the provision of daylight reserves (also called daylight credit) and then shrinking the supply back at the end of the day to be consistent with the desired market interest rate.
So the central bank must ensure that all private cheques (that are funded) clear and other interbank transactions occur smoothly as part of its role of maintaining financial stability. But, equally, it must also maintain the bank reserves in aggregate at a level that is consistent with its target policy setting given the relationship between the two.
So operating factors link the level of reserves to the monetary policy setting under certain circumstances. These circumstances require that the return on “excess” reserves held by the banks is below the monetary policy target rate. In addition to setting a lending rate (discount rate), the central bank also sets a support rate which is paid on commercial bank reserves held by the central bank.
Many countries (such as Australia and Canada) maintain a default return on surplus reserve accounts (for example, the Reserve Bank of Australia pays a default return equal to 25 basis points less than the overnight rate on surplus Exchange Settlement accounts). Other countries like the US and Japan have historically offered a zero return on reserves which means persistent excess liquidity would drive the short-term interest rate to zero.
The support rate effectively becomes the interest-rate floor for the economy. If the short-run or operational target interest rate, which represents the current monetary policy stance, is set by the central bank between the discount and support rate. This effectively creates a corridor or a spread within which the short-term interest rates can fluctuate with liquidity variability. It is this spread that the central bank manages in its daily operations.
So the issue then becomes – at what level should the support rate be set? To answer that question, I reproduce a version of teh diagram from the FRBNY paper which outlined a simple model of the way in which reserves are manipulated by the central bank as part of its liquidity management operations designed to implement a specific monetary policy target (policy interest rate setting).
I describe the FRBNY model in detail in the blog – Understanding central bank operations so I won’t repeat that explanation.
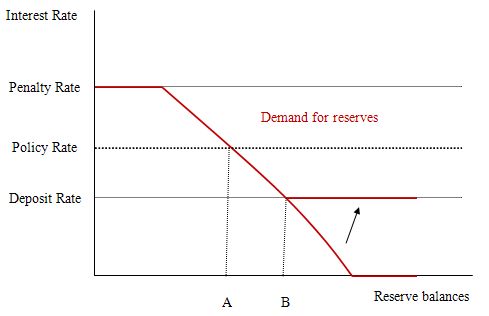
The penalty rate is the rate the central bank charges for loans to banks to cover shortages of reserves. If the interbank rate is at the penalty rate then the banks will be indifferent as to where they access reserves from so the demand curve is horizontal (shown in red).
Once the price of reserves falls below the penalty rate, banks will then demand reserves according to their requirments (the legal and the perceived). The higher the market rate of interest, the higher is the opportunity cost of holding reserves and hence the lower will be the demand. As rates fall, the opportunity costs fall and the demand for reserves increases. But in all cases, banks will only seek to hold (in aggregate) the levels consistent with their requirements.
At low interest rates (say zero) banks will hold the legally-required reserves plus a buffer that ensures there is no risk of falling short during the operation of the payments system.
Commercial banks choose to hold reserves to ensure they can meet all their obligations with respect to the clearing house (payments) system. Because there is considerable uncertainty (for example, late-day payment flows after the interbank market has closed), a bank may find itself short of reserves. Depending on the circumstances, it may choose to keep a buffer stock of reserves just to meet these contingencies.
So central bank reserves are intrinsic to the payments system where a mass of interbank claims are resolved by manipulating the reserve balances that the banks hold at the central bank. This process has some expectational regularity on a day-to-day basis but stochastic (uncertain) demands for payments also occur which means that banks will hold surplus reserves to avoid paying any penalty arising from having reserve deficiencies at the end of the day (or accounting period).
To understand what is going on not that the diagram is representing the system-wide demand for bank reserves where the horizontal axis measures the total quantity of reserve balances held by banks while the vertical axis measures the market interest rate for overnight loans of these balances
In this diagram there are no required reserves (to simplify matters). We also initially, abstract from the deposit rate for the time being to understand what role it plays if we introduce it.
Without the deposit rate, the central bank has to ensure that it supplies enough reserves to meet demand while still maintaining its policy rate (the monetary policy setting.
So the model can demonstrate that the market rate of interest will be determined by the central bank supply of reserves. So the level of reserves supplied by the central bank supply brings the market rate of interest into line with the policy target rate.
At the supply level shown as Point A, the central bank can hit its monetary policy target rate of interest given the banks’ demand for aggregate reserves. So the central bank announces its target rate then undertakes monetary operations (liquidity management operations) to set the supply of reserves to this target level.
So contrary to what Mankiw’s textbook tells students the reality is that monetary policy is about changing the supply of reserves in such a way that the market rate is equal to the policy rate.
The central bank uses open market operations to manipulate the reserve level and so must be buying and selling government debt to add or drain reserves from the banking system in line with its policy target.
If there are excess reserves in the system and the central bank didn’t intervene then the market rate would drop towards zero and the central bank would lose control over its target rate (that is, monetary policy would be compromised).
As explained in the blog – Understanding central bank operations – the introduction of a support rate payment (deposit rate) whereby the central bank pays the member banks a return on reserves held overnight changes things considerably.
It clearly can – under certain circumstances – eliminate the need for any open-market operations to manage the volume of bank reserves.
In terms of the diagram, the major impact of the deposit rate is to lift the rate at which the demand curve becomes horizontal (as depicted by the new horizontal red segment moving up via the arrow).
This policy change allows the banks to earn overnight interest on their excess reserve holdings and becomes the minimum market interest rate and defines the lower bound of the corridor within which the market rate can fluctuate without central bank intervention.
So in this diagram, the market interest rate is still set by the supply of reserves (given the demand for reserves) and so the central bank still has to manage reserves appropriately to ensure it can hit its policy target.
If there are excess reserves in the system in this case, and the central bank didn’t intervene, then the market rate will drop to the support rate (at Point B).
So if the central bank wants to maintain control over its target rate it can either set a support rate below the desired policy rate (as in Australia) and then use open market operations to ensure the reserve supply is consistent with Point A or set the support rate equal to the target policy rate.
The answer to the question is thus True because it all depends on where the support rate is set. Only if it set equal to the policy rate will there be no need for the central bank to manage liquidity via open market operations.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Understanding central bank operations
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- It is a pity that he doesn’t know the answer himself
Premium Question 5:
Mainstream economists have argued that the large scale quantitative easing conducted by central banks in recent years – so-called printing money – would be inflationary. They base their predictions on the Quantity Theory of Money which links the growth of the money stock to the inflation rate (too much money chasing too few goods). The fact that inflation is in retreat despite these programs does not refute the mainstream economic theory of inflation.
The answer is True.
The question requires you to: (a) understand the Quantity Theory of Money; and (b) understand the impact of quantitative easing in relation to Quantity Theory of Money.
The short reason the answer is true is that quantitative easing has not increased the aggregates that drive the alleged causality in the Quantity Theory of Money – that is, the various estimates of the “money supply”.
The Quantity Theory of Money which in symbols is MV = PQ but means that the money stock times the turnover per period (V) is equal to the price level (P) times real output (Q). The mainstream assume that V is fixed (despite empirically it moving all over the place) and Q is always at full employment as a result of market adjustments.
Yes, in applying this theory they deny the existence of unemployment. The more reasonable mainstream economists (who probably have kids who cannot get a job at present) admit that short-run deviations in the predictions of the Quantity Theory of Money can occur but in the long-run all the frictions causing unemployment will disappear and the theory will apply.
In general, the Monetarists (the most recent group to revive the Quantity Theory of Money) claim that with V and Q fixed, then changes in M cause changes in P – which is the basic Monetarist claim that expanding the money supply is inflationary. They say that excess monetary growth creates a situation where too much money is chasing too few goods and the only adjustment that is possible is nominal (that is, inflation).
One of the contributions of Keynes was to show the Quantity Theory of Money could not be correct. He observed price level changes independent of monetary supply movements (and vice versa) which changed his own perception of the way the monetary system operated.
Further, with high rates of capacity and labour underutilisation at various times (including now) one can hardly seriously maintain the view that Q is fixed. There is always scope for real adjustments (that is, increasing output) to match nominal growth in aggregate demand. So if increased credit became available and borrowers used the deposits that were created by the loans to purchase goods and services, it is likely that firms with excess capacity will re
The mainstream have related the current non-standard monetary policy efforts – the so-called quantitative easing – to the Quantity Theory of Money and predicted hyperinflation will arise.
So it is the modern belief in the Quantity Theory of Money is behind the hysteria about the level of bank reserves at present – it has to be inflationary they say because there is all this money lying around and it will flood the economy.
Textbook like that of Mankiw mislead their students into thinking that there is a direct relationship between the monetary base and the money supply. They claim that the central bank “controls the money supply by buying and selling government bonds in open-market operations” and that the private banks then create multiples of the base via credit-creation.
Students are familiar with the pages of textbook space wasted on explaining the erroneous concept of the money multiplier where a banks are alleged to “loan out some of its reserves and create money”. As I have indicated several times the depiction of the fractional reserve-money multiplier process in textbooks like Mankiw exemplifies the mainstream misunderstanding of banking operations. Please read my blog – Money multiplier and other myths – for more discussion on this point.
The idea that the monetary base (the sum of bank reserves and currency) leads to a change in the money supply via some multiple is not a valid representation of the way the monetary system operates even though it appears in all mainstream macroeconomics textbooks and is relentlessly rammed down the throats of unsuspecting economic students.
The money multiplier myth leads students to think that as the central bank can control the monetary base then it can control the money supply. Further, given that inflation is allegedly the result of the money supply growing too fast then the blame is sheeted home to the “government” (the central bank in this case).
The reality is that the central bank does not have the capacity to control the money supply. We have regularly traversed this point. In the world we live in, bank loans create deposits and are made without reference to the reserve positions of the banks. The bank then ensures its reserve positions are legally compliant as a separate process knowing that it can always get the reserves from the central bank.
The only way that the central bank can influence credit creation in this setting is via the price of the reserves it provides on demand to the commercial banks.
So when we talk about quantitative easing, we must first understand that it requires the short-term interest rate to be at zero or close to it. Otherwise, the central bank would not be able to maintain control of a positive interest rate target because the excess reserves would invoke a competitive process in the interbank market which would effectively drive the interest rate down.
Quantitative easing then involves the central bank buying assets from the private sector – government bonds and high quality corporate debt. So what the central bank is doing is swapping financial assets with the banks – they sell their financial assets and receive back in return extra reserves. So the central bank is buying one type of financial asset (private holdings of bonds, company paper) and exchanging it for another (reserve balances at the central bank). The net financial assets in the private sector are in fact unchanged although the portfolio composition of those assets is altered (maturity substitution) which changes yields and returns.
In terms of changing portfolio compositions, quantitative easing increases central bank demand for “long maturity” assets held in the private sector which reduces interest rates at the longer end of the yield curve. These are traditionally thought of as the investment rates. This might increase aggregate demand given the cost of investment funds is likely to drop. But on the other hand, the lower rates reduce the interest-income of savers who will reduce consumption (demand) accordingly.
How these opposing effects balance out is unclear but the evidence suggests there is not very much impact at all.
For the monetary aggregates (outside of base money) to increase, the banks would then have to increase their lending and create deposits. This is at the heart of the mainstream belief is that quantitative easing will stimulate the economy sufficiently to put a brake on the downward spiral of lost production and the increasing unemployment. The recent experience (and that of Japan in 2001) showed that quantitative easing does not succeed in doing this.
Should we be surprised. Definitely not. The mainstream view is based on the erroneous belief that the banks need reserves before they can lend and that quantitative easing provides those reserves. That is a major misrepresentation of the way the banking system actually operates. But the mainstream position asserts (wrongly) that banks only lend if they have prior reserves.
The illusion is that a bank is an institution that accepts deposits to build up reserves and then on-lends them at a margin to make money. The conceptualisation suggests that if it doesn’t have adequate reserves then it cannot lend. So the presupposition is that by adding to bank reserves, quantitative easing will help lending.
But banks do not operate like this. Bank lending is not “reserve constrained”. Banks lend to any credit worthy customer they can find and then worry about their reserve positions afterwards. If they are short of reserves (their reserve accounts have to be in positive balance each day and in some countries central banks require certain ratios to be maintained) then they borrow from each other in the interbank market or, ultimately, they will borrow from the central bank through the so-called discount window. They are reluctant to use the latter facility because it carries a penalty (higher interest cost).
The point is that building bank reserves will not increase the bank’s capacity to lend. Loans create deposits which generate reserves.
The reason that the commercial banks are currently not lending much is because they are not convinced there are credit worthy customers on their doorstep. In the current climate the assessment of what is credit worthy has become very strict compared to the lax days as the top of the boom approached.
Those that claim that quantitative easing will expose the economy to uncontrollable inflation are just harking back to the old and flawed Quantity Theory of Money. This theory has no application in a modern monetary economy and proponents of it have to explain why economies with huge excess capacity to produce (idle capital and high proportions of unused labour) cannot expand production when the orders for goods and services increase. Should quantitative easing actually stimulate spending then the depressed economies will likely respond by increasing output not prices.
So the fact that large scale quantitative easing conducted by central banks in Japan in 2001 and now in the UK and the USA has not caused inflation does not provide a strong refutation of the mainstream Quantity Theory of Money because it has not impacted on the monetary aggregates.
The fact that is hasn’t is not surprising if you understand how the monetary system operates but it has certainly bedazzled the (easily dazzled) mainstream economists.
The proposition that is refuted by the recent evidence is that of the money multiplier.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:

The explanation for Question 5 has left me quite confused Bill. I seem to be missing something.
I answered False (shown as the incorrect choice) but most of the explanation suggests to me that False might’ve been the correct answer (?)
Indeed, you say “The short reason the answer is false…” up front in the explanation [Bill Edit – changed to true – thanks]
But you conclude by saying that “the proposition that is refuted by the recent evidence is that of the money multiplier.”
The failure of the QE programs to cause inflation certainly refutes the proposition of the money multiplier (as you say) but isn’t the money multiplier part and parcel of the QTM, the mainstream argument ?