Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – April 23, 2011 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
Even Modern Monetary Theory accepts that continually expanding the money supply will inevitably be inflationary.
The answer is False.
The question requires you to: (a) understand the difference between bank reserves and the money supply; and (b) understand the Quantity Theory of Money.
The mainstream macroeconomics text book argument that increasing the money supply will cause inflation is based on the Quatity Theory of Money. First, expanding bank reserves will put more base money into the economy but not increase the aggregates that drive the alleged causality in the Quantity Theory of Money – that is, the various estimates of the “money supply”.
Second, even if the money supply is increasing, the economy may still adjust to that via output and income increases up to full capacity. Over time, as investment expands the productive capacity of the economy, aggregate demand growth can support the utilisation of that increased capacity without there being inflation.
In this situation, an increasing money supply (which is really not a very useful aggregate at all) which signals expanding credit will not be inflationary.
So the Maybe relates to the situation that might arise if nominal demand kept increasing beyond the capacity of the real economy to absorb it via increased production. Then you would get inflation and the “value” of the dollar would start to decline.
The Quantity Theory of Money which in symbols is MV = PQ but means that the money stock times the turnover per period (V) is equal to the price level (P) times real output (Q). The mainstream assume that V is fixed (despite empirically it moving all over the place) and Q is always at full employment as a result of market adjustments.
In applying this theory the mainstream deny the existence of unemployment. The more reasonable mainstream economists admit that short-run deviations in the predictions of the Quantity Theory of Money can occur but in the long-run all the frictions causing unemployment will disappear and the theory will apply.
In general, the Monetarists (the most recent group to revive the Quantity Theory of Money) claim that with V and Q fixed, then changes in M cause changes in P – which is the basic Monetarist claim that expanding the money supply is inflationary. They say that excess monetary growth creates a situation where too much money is chasing too few goods and the only adjustment that is possible is nominal (that is, inflation).
One of the contributions of Keynes was to show the Quantity Theory of Money could not be correct. He observed price level changes independent of monetary supply movements (and vice versa) which changed his own perception of the way the monetary system operated.
Further, with high rates of capacity and labour underutilisation at various times (including now) one can hardly seriously maintain the view that Q is fixed. There is always scope for real adjustments (that is, increasing output) to match nominal growth in aggregate demand. So if increased credit became available and borrowers used the deposits that were created by the loans to purchase goods and services, it is likely that firms with excess capacity will react to the increased nominal demand by increasing output.
The mainstream have related the current non-standard monetary policy efforts – the so-called quantitative easing – to the Quantity Theory of Money and predicted hyperinflation will arise.
So it is the modern belief in the Quantity Theory of Money is behind the hysteria about the level of bank reserves at present – it has to be inflationary they say because there is all this money lying around and it will flood the economy.
Textbook like that of Mankiw mislead their students into thinking that there is a direct relationship between the monetary base and the money supply. They claim that the central bank “controls the money supply by buying and selling government bonds in open-market operations” and that the private banks then create multiples of the base via credit-creation.
Students are familiar with the pages of textbook space wasted on explaining the erroneous concept of the money multiplier where a banks are alleged to “loan out some of its reserves and create money”. As I have indicated several times the depiction of the fractional reserve-money multiplier process in textbooks like Mankiw exemplifies the mainstream misunderstanding of banking operations. Please read my blog – Money multiplier and other myths – for more discussion on this point.
The idea that the monetary base (the sum of bank reserves and currency) leads to a change in the money supply via some multiple is not a valid representation of the way the monetary system operates even though it appears in all mainstream macroeconomics textbooks and is relentlessly rammed down the throats of unsuspecting economic students.
The money multiplier myth leads students to think that as the central bank can control the monetary base then it can control the money supply. Further, given that inflation is allegedly the result of the money supply growing too fast then the blame is sheeted home to the “government” (the central bank in this case).
The reality is that the central bank does not have the capacity to control the money supply. We have regularly traversed this point. In the world we live in, bank loans create deposits and are made without reference to the reserve positions of the banks. The bank then ensures its reserve positions are legally compliant as a separate process knowing that it can always get the reserves from the central bank.
The only way that the central bank can influence credit creation in this setting is via the price of the reserves it provides on demand to the commercial banks.
So when we talk about quantitative easing, we must first understand that it requires the short-term interest rate to be at zero or close to it. Otherwise, the central bank would not be able to maintain control of a positive interest rate target because the excess reserves would invoke a competitive process in the interbank market which would effectively drive the interest rate down.
Quantitative easing then involves the central bank buying assets from the private sector – government bonds and high quality corporate debt. So what the central bank is doing is swapping financial assets with the banks – they sell their financial assets and receive back in return extra reserves. So the central bank is buying one type of financial asset (private holdings of bonds, company paper) and exchanging it for another (reserve balances at the central bank). The net financial assets in the private sector are in fact unchanged although the portfolio composition of those assets is altered (maturity substitution) which changes yields and returns.
In terms of changing portfolio compositions, quantitative easing increases central bank demand for “long maturity” assets held in the private sector which reduces interest rates at the longer end of the yield curve. These are traditionally thought of as the investment rates. This might increase aggregate demand given the cost of investment funds is likely to drop. But on the other hand, the lower rates reduce the interest-income of savers who will reduce consumption (demand) accordingly.
How these opposing effects balance out is unclear but the evidence suggests there is not very much impact at all.
For the monetary aggregates (outside of base money) to increase, the banks would then have to increase their lending and create deposits. This is at the heart of the mainstream belief is that quantitative easing will stimulate the economy sufficiently to put a brake on the downward spiral of lost production and the increasing unemployment. The recent experience (and that of Japan in 2001) showed that quantitative easing does not succeed in doing this.
This should come as no surprise at all if you understand Modern Monetary Theory (MMT).
The mainstream view is based on the erroneous belief that the banks need reserves before they can lend and that quantitative easing provides those reserves. That is a major misrepresentation of the way the banking system actually operates. But the mainstream position asserts (wrongly) that banks only lend if they have prior reserves.
The illusion is that a bank is an institution that accepts deposits to build up reserves and then on-lends them at a margin to make money. The conceptualisation suggests that if it doesn’t have adequate reserves then it cannot lend. So the presupposition is that by adding to bank reserves, quantitative easing will help lending.
But banks do not operate like this. Bank lending is not “reserve constrained”. Banks lend to any credit worthy customer they can find and then worry about their reserve positions afterwards. If they are short of reserves (their reserve accounts have to be in positive balance each day and in some countries central banks require certain ratios to be maintained) then they borrow from each other in the interbank market or, ultimately, they will borrow from the central bank through the so-called discount window. They are reluctant to use the latter facility because it carries a penalty (higher interest cost).
The point is that building bank reserves will not increase the bank’s capacity to lend. Loans create deposits which generate reserves.
The reason that the commercial banks are currently not lending much is because they are not convinced there are credit worthy customers on their doorstep. In the current climate the assessment of what is credit worthy has become very strict compared to the lax days as the top of the boom approached.
Those that claim that quantitative easing will expose the economy to uncontrollable inflation are just harking back to the old and flawed Quantity Theory of Money. This theory has no application in a modern monetary economy and proponents of it have to explain why economies with huge excess capacity to produce (idle capital and high proportions of unused labour) cannot expand production when the orders for goods and services increase. Should quantitative easing actually stimulate spending then the depressed economies will likely respond by increasing output not prices.
So the fact that large scale quantitative easing conducted by central banks in Japan in 2001 and now in the UK and the USA has not caused inflation does not provide a strong refutation of the mainstream Quantity Theory of Money because it has not impacted on the monetary aggregates.
The fact that is hasn’t is not surprising if you understand how the monetary system operates but it has certainly bedazzled the (easily dazzled) mainstream economists.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Money multiplier and other myths
- Islands in the sun
- Operation twist – then and now
- Quantitative easing 101
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
Question 2:
If there is an external deficit of 2 per cent of GDP and the government balances its budget then the private sector will have
(a) an excess of spending relative to its income equal to 2 per cent of GDP.
(b) a deficit in spending relative to its income equal to 2 per cent of GDP.
(c) Cannot really tell definitively without further information.
The correct answer is Option (a) – “an excess of spending relative to its income overall equal to 2 per cent of GDP”.
This is a question about the sectoral balances – the government budget balance, the external balance and the private domestic balance – that have to always add to zero because they are derived as an accounting identity from the national accounts. The balances reflect the underlying economic behaviour in each sector which is interdependent – given this is a macroeconomic system we are considering.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero. The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (I – S) – positive if in deficit, negative if in surplus.
- The Budget Deficit (G – T) – negative if in surplus, positive if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
A simplification is to add (I – S) + (X – M) and call it the non-government sector. Then you get the basic result that the government balance equals exactly $-for-$ (absolutely or as a per cent of GDP) the non-government balance (the sum of the private domestic and external balances).
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
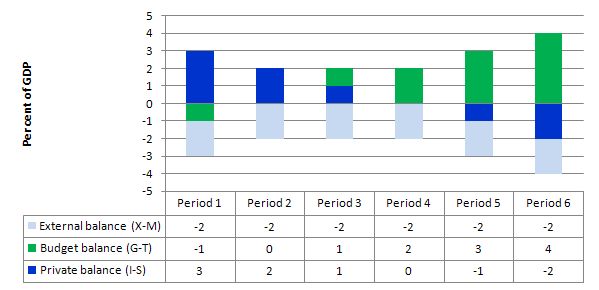
The following graph with accompanying data table lets you see the evolution of the balances expressed in terms of percent of GDP. I have held the external deficit constant at 2 per cent of GDP.
To aid interpretation remember that (I-S) > 0 means that the private domestic sector is spending more than they are earning; that (G-T) < 0 means that the government is running a surplus because T > G; and (X-M) < 0 means the external position is in deficit because imports are greater than exports.
If we assume these Periods are average positions over the course of each business cycle (that is, Period 1 is a separate business cycle to Period 2 etc).
In Period 1, there is an external deficit (2 per cent of GDP), a budget surplus of 1 per cent of GDP and the private sector is in deficit (I > S) to the tune of 3 per cent of GDP.
In Period 2, as the government budget enters balance (presumably the government increased spending or cut taxes or the automatic stabilisers were working), the private domestic deficit narrows and now equals the external deficit. This is the case that the question is referring to.
So this is the situation described in the Question which means that the private sector is running an overall deficit – so incurring an “excess of spending over its income overall equal to 2 per cent of GDP”.
This provides another important rule with the deficit terorists typically overlook – that if a nation records an average external deficit over the course of the business cycle (peak to peak) and you succeed in balancing the public budget then the private domestic sector will be in deficit equal to the external deficit. That means, the private sector is increasingly building debt to fund its “excess expenditure”. That conclusion is inevitable when you balance a budget with an external deficit. It could never be a viable fiscal rule.
In Periods 3 and 4, the budget deficit rises from balance to 1 to 2 per cent of GDP and the private domestic balance moves towards surplus. At the end of Period 4, the private sector is spending as much as they earning.
Periods 5 and 6 show the benefits of budget deficits when there is an external deficit. The private sector now is able to generate surpluses overall (that is, save as a sector) as a result of the public deficit.
So what is the economics that underpin these different situations?
If the nation is running an external deficit it means that the contribution to aggregate demand from the external sector is negative – that is net drain of spending – dragging output down.
The external deficit also means that foreigners are increasing financial claims denominated in the local currency. Given that exports represent a real cost and imports a real benefit, the motivation for a nation running a net exports surplus (the exporting nation in this case) must be to accumulate financial claims (assets) denominated in the currency of the nation running the external deficit.
A fiscal surplus also means the government is spending less than it is “earning” and that puts a drag on aggregate demand and constrains the ability of the economy to grow.
In these circumstances, for income to be stable, the private domestic sector has to spend more than they earn.
You can see this by going back to the aggregate demand relations above. For those who like simple algebra we can manipulate the aggregate demand model to see this more clearly.
Y = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that the total national income (Y or GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
So if the G is spending less than it is “earning” and the external sector is adding less income (X) than it is absorbing spending (M), then the other spending components must be greater than total income.
Only when the government budget deficit supports aggregate demand at income levels which permit the private sector to save out of that income will the latter achieve its desired outcome. At this point, income and employment growth are maximised and private debt levels will be stable.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Barnaby, better to walk before we run
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
Question 3:
By draining funds out of the system, government borrowing from the private sector reduces the risk that public spending will overheat the economy.
The answer is false.
The mainstream macroeconomic textbooks all have a chapter on fiscal policy (and it is often written in the context of the so-called IS-LM model but not always).
The chapters always introduces the so-called Government Budget Constraint that alleges that governments have to “finance” all spending either through taxation; debt-issuance; or money creation. The writer fails to understand that government spending is performed in the same way irrespective of the accompanying monetary operations.
The textbook argument claims that money creation (borrowing from central bank) is inflationary while the latter (private bond sales) is less so. These conclusions are based on their erroneous claim that “money creation” adds more to aggregate demand than bond sales, because the latter forces up interest rates which crowd out some private spending.
All these claims are without foundation in a fiat monetary system and an understanding of the banking operations that occur when governments spend and issue debt helps to show why.
So what would happen if a sovereign, currency-issuing government (with a flexible exchange rate) ran a budget deficit without issuing debt?
Like all government spending, the Treasury would credit the reserve accounts held by the commercial bank at the central bank. The commercial bank in question would be where the target of the spending had an account. So the commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a deposit would be made.
The transactions are clear: The commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a new deposit has been made.
Further, the target of the fiscal initiative enjoys increased assets (bank deposit) and net worth (a liability/equity entry on their balance sheet).
Taxation does the opposite and so a deficit (spending greater than taxation) means that reserves increase and private net worth increases.
This means that there are likely to be excess reserves in the “cash system” which then raises issues for the central bank about its liquidity management. The aim of the central bank is to “hit” a target interest rate and so it has to ensure that competitive forces in the interbank market do not compromise that target.
When there are excess reserves there is downward pressure on the overnight interest rate (as banks scurry to seek interest-earning opportunities), the central bank then has to sell government bonds to the banks to soak the excess up and maintain liquidity at a level consistent with the target.
Some central banks offer a return on overnight reserves which reduces the need to sell debt as a liquidity management operation.
There is no sense that these debt sales have anything to do with “financing” government net spending. The sales are a monetary operation aimed at interest-rate maintenance.
So M1 (deposits in the non-government sector) rise as a result of the deficit without a corresponding increase in liabilities. It is this result that leads to the conclusion that that deficits increase net financial assets in the non-government sector.
What would happen if there were bond sales? All that happens is that the banks reserves are reduced by the bond sales but this does not reduce the deposits created by the net spending. So net worth is not altered. What is changed is the composition of the asset portfolio held in the non-government sector.
The only difference between the Treasury “borrowing from the central bank” and issuing debt to the private sector is that the central bank has to use different operations to pursue its policy interest rate target. If it debt is not issued to match the deficit then it has to either pay interest on excess reserves (which most central banks are doing now anyway) or let the target rate fall to zero (the Japan solution).
There is no difference to the impact of the deficits on net worth in the non-government sector.
Mainstream economists would say that by draining the reserves, the central bank has reduced the ability of banks to lend which then, via the money multiplier, expands the money supply.
However, the reality is that:
- Building bank reserves does not increase the ability of the banks to lend.
- The money multiplier process so loved by the mainstream does not describe the way in which banks make loans.
- Inflation is caused by aggregate demand growing faster than real output capacity. The reserve position of the banks is not functionally related with that process.
So the banks are able to create as much credit as they can find credit-worthy customers to hold irrespective of the operations that accompany government net spending.
This doesn’t lead to the conclusion that deficits do not carry an inflation risk. All components of aggregate demand carry an inflation risk if they become excessive, which can only be defined in terms of the relation between spending and productive capacity.
It is totally fallacious to think that private placement of debt reduces the inflation risk. It does not.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
- Why history matters
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- The complacent students sit and listen to some of that
Question 4:
A national government would be unable to rely on the central bank purchasing treasury debt to match its budget deficit (that is, “monetise the deficit”) if the central bank is targeting a positive short-term policy rate.
The answer is False.
The central bank conducts what are called liquidity management operations for two reasons. First, it has to ensure that all private cheques (that are funded) clear and other interbank transactions occur smoothly as part of its role of maintaining financial stability. Second, it must maintain aggregate bank reserves at a level that is consistent with its target policy setting given the relationship between the two.
So operating factors link the level of reserves to the monetary policy setting under certain circumstances. These circumstances require that the return on “excess” reserves held by the banks is below the monetary policy target rate. In addition to setting a lending rate (discount rate), the central bank also sets a support rate which is paid on commercial bank reserves held by the central bank.
Commercial banks maintain accounts with the central bank which permit reserves to be managed and also the clearing system to operate smoothly. In addition to setting a lending rate (discount rate), the central bank also can set a support rate which is paid on commercial bank reserves held by the central bank (which might be zero).
Many countries (such as Australia, Canada and zones such as the European Monetary Union) maintain a default return on surplus reserve accounts (for example, the Reserve Bank of Australia pays a default return equal to 25 basis points less than the overnight rate on surplus Exchange Settlement accounts). Other countries like Japan and the US have typically not offered a return on reserves until the onset of the current crisis.
If the support rate is zero then persistent excess liquidity in the cash system (excess reserves) will instigate dynamic forces which would drive the short-term interest rate to zero unless the government sells bonds (or raises taxes). This support rate becomes the interest-rate floor for the economy.
The short-run or operational target interest rate, which represents the current monetary policy stance, is set by the central bank between the discount and support rate. This effectively creates a corridor or a spread within which the short-term interest rates can fluctuate with liquidity variability. It is this spread that the central bank manages in its daily operations.
In most nations, commercial banks by law have to maintain positive reserve balances at the central bank, accumulated over some specified period. At the end of each day commercial banks have to appraise the status of their reserve accounts. Those that are in deficit can borrow the required funds from the central bank at the discount rate.
Alternatively banks with excess reserves are faced with earning the support rate which is below the current market rate of interest on overnight funds if they do nothing. Clearly it is profitable for banks with excess funds to lend to banks with deficits at market rates. Competition between banks with excess reserves for custom puts downward pressure on the short-term interest rate (overnight funds rate) and depending on the state of overall liquidity may drive the interbank rate down below the operational target interest rate. When the system is in surplus overall this competition would drive the rate down to the support rate.
The main instrument of this liquidity management is through open market operations, that is, buying and selling government debt. When the competitive pressures in the overnight funds market drives the interbank rate below the desired target rate, the central bank drains liquidity by selling government debt. This open market intervention therefore will result in a higher value for the overnight rate. Importantly, we characterise the debt-issuance as a monetary policy operation designed to provide interest-rate maintenance. This is in stark contrast to orthodox theory which asserts that debt-issuance is an aspect of fiscal policy and is required to finance deficit spending.
So the fundamental principles that arise in a fiat monetary system are as follows.
- The central bank sets the short-term interest rate based on its policy aspirations.
- Government spending is independent of borrowing which the latter best thought of as coming after spending.
- Government spending provides the net financial assets (bank reserves) which ultimately represent the funds used by the non-government agents to purchase the debt.
- Budget deficits put downward pressure on interest rates contrary to the myths that appear in macroeconomic textbooks about ‘crowding out’.
- The “penalty for not borrowing” is that the interest rate will fall to the bottom of the “corridor” prevailing in the country which may be zero if the central bank does not offer a return on reserves.
- Government debt-issuance is a “monetary policy” operation rather than being intrinsic to fiscal policy, although in a modern monetary paradigm the distinctions between monetary and fiscal policy as traditionally defined are moot.
Accordingly, debt is issued as an interest-maintenance strategy by the central bank. It has no correspondence with any need to fund government spending. Debt might also be issued if the government wants the private sector to have less purchasing power.
Further, the idea that governments would simply get the central bank to “monetise” treasury debt (which is seen orthodox economists as the alternative “financing” method for government spending) is highly misleading. Debt monetisation is usually referred to as a process whereby the central bank buys government bonds directly from the treasury.
In other words, the federal government borrows money from the central bank rather than the public. Debt monetisation is the process usually implied when a government is said to be printing money. Debt monetisation, all else equal, is said to increase the money supply and can lead to severe inflation.
However, as long as the central bank has a mandate to maintain a target short-term interest rate, the size of its purchases and sales of government debt are not discretionary. Once the central bank sets a short-term interest rate target, its portfolio of government securities changes only because of the transactions that are required to support the target interest rate.
The central bank’s lack of control over the quantity of reserves underscores the impossibility of debt monetisation. The central bank is unable to monetise the federal debt by purchasing government securities at will because to do so would cause the short-term target rate to fall to zero or to the support rate. If the central bank purchased securities directly from the treasury and the treasury then spent the money, its expenditures would be excess reserves in the banking system. The central bank would be forced to sell an equal amount of securities to support the target interest rate.
The central bank would act only as an intermediary. The central bank would be buying securities from the treasury and selling them to the public. No monetisation would occur.
However, the central bank may agree to pay the short-term interest rate to banks who hold excess overnight reserves. This would eliminate the need by the commercial banks to access the interbank market to get rid of any excess reserves and would allow the central bank to maintain its target interest rate without issuing debt.
In these cases, it could buy all the treasury debt without consequences for its policy target.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- The consolidated government – treasury and central bank
- Saturday Quiz – May 1, 2010 – answers and discussion
- Understanding central bank operations
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- Deficit spending 101 – Part 1
- Deficit spending 101 – Part 2
- Deficit spending 101 – Part 3
Question 5 – Premium question
In Year 1, the economy plunges into recession with nominal GDP growth falling to minus -1 per cent. The inflation rate is subdued at 1 per cent per annum. The outstanding public debt is equal to the value of the nominal GDP and the nominal interest rate is equal to 1 per cent (and this is the rate the government pays on all outstanding debt). The government’s budget balance net of interest payments goes into deficit equivalent to 1 per cent of GDP and the debt ratio rises by 3 per cent. In Year 2, the government stimulates the economy and pushes the primary budget deficit out to 2 per cent of GDP and in doing so stimulates aggregate demand and the economy records a 4 per cent nominal GDP growth rate. All other parameters are unchanged in Year 2. Under these circumstances, the public debt ratio:
(a) rises by 1 per cent.
(b) falls by 1 per cent.
(c) falls but you cannot tell by how much from this information.
(d) none of the above.
The answer is Option (b) – “none of the above.”.
This question requires you to understand the key parameters and relationships that determine the dynamics of the public debt ratio. An understanding of these relationships allows you to debunk statements that are made by those who think fiscal austerity will allow a government to reduce its public debt ratio.
While Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) places no particular importance in the public debt to GDP ratio for a sovereign government, given that insolvency is not an issue, the mainstream debate is dominated by the concept.
The unnecessary practice of fiat currency-issuing governments of issuing public debt $-for-$ to match public net spending (deficits) ensures that the debt levels will rise when there are deficits.
Rising deficits usually mean declining economic activity (especially if there is no evidence of accelerating inflation) which suggests that the debt/GDP ratio may be rising because the denominator is also likely to be falling or rising below trend.
Further, historical experience tells us that when economic growth resumes after a major recession, during which the public debt ratio can rise sharply, the latter always declines again.
It is this endogenous nature of the ratio that suggests it is far more important to focus on the underlying economic problems which the public debt ratio just mirrors.
Mainstream economics starts with the flawed analogy between the household and the sovereign government such that any excess in government spending over taxation receipts has to be “financed” in two ways: (a) by borrowing from the public; and/or (b) by “printing money”.
Neither characterisation is remotely representative of what happens in the real world in terms of the operations that define transactions between the government and non-government sector.
Further, the basic analogy is flawed at its most elemental level. The household must work out the financing before it can spend. The household cannot spend first. The government can spend first and ultimately does not have to worry about financing such expenditure.
However, in mainstream (dream) land, the framework for analysing these so-called “financing” choices is called the government budget constraint (GBC). The GBC says that the budget deficit in year t is equal to the change in government debt over year t plus the change in high powered money over year t. So in mathematical terms it is written as:
which you can read in English as saying that Budget deficit = Government spending + Government interest payments – Tax receipts must equal (be “financed” by) a change in Bonds (B) and/or a change in high powered money (H). The triangle sign (delta) is just shorthand for the change in a variable.
However, this is merely an accounting statement. In a stock-flow consistent macroeconomics, this statement will always hold. That is, it has to be true if all the transactions between the government and non-government sector have been corrected added and subtracted.
So in terms of MMT, the previous equation is just an ex post accounting identity that has to be true by definition and has not real economic importance.
But for the mainstream economist, the equation represents an ex ante (before the fact) financial constraint that the government is bound by. The difference between these two conceptions is very significant and the second (mainstream) interpretation cannot be correct if governments issue fiat currency (unless they place voluntary constraints on themselves to act as if it is).
Further, in mainstream economics, money creation is erroneously depicted as the government asking the central bank to buy treasury bonds which the central bank in return then prints money. The government then spends this money.
This is called debt monetisation and you can find out why this is typically not a viable option for a central bank by reading the Deficits 101 suite – Deficit spending 101 – Part 1 – Deficit spending 101 – Part 2 – Deficit spending 101 – Part 3.
Anyway, the mainstream claims that if governments increase the money growth rate (they erroneously call this “printing money”) the extra spending will cause accelerating inflation because there will be “too much money chasing too few goods”! Of-course, we know that proposition to be generally preposterous because economies that are constrained by deficient demand (defined as demand below the full employment level) respond to nominal demand increases by expanding real output rather than prices. There is an extensive literature pointing to this result.
So when governments are expanding deficits to offset a collapse in private spending, there is plenty of spare capacity available to ensure output rather than inflation increases.
But not to be daunted by the “facts”, the mainstream claim that because inflation is inevitable if “printing money” occurs, it is unwise to use this option to “finance” net public spending.
Hence they say as a better (but still poor) solution, governments should use debt issuance to “finance” their deficits. Thy also claim this is a poor option because in the short-term it is alleged to increase interest rates and in the longer-term is results in higher future tax rates because the debt has to be “paid back”.
Neither proposition bears scrutiny – you can read these blogs – Will we really pay higher taxes? and Will we really pay higher interest rates? – for further discussion on these points.
The mainstream textbooks are full of elaborate models of debt pay-back, debt stabilisation etc which all claim (falsely) to “prove” that the legacy of past deficits is higher debt and to stabilise the debt, the government must eliminate the deficit which means it must then run a primary surplus equal to interest payments on the existing debt.
A primary budget balance is the difference between government spending (excluding interest rate servicing) and taxation revenue.
The standard mainstream framework, which even the so-called progressives (deficit-doves) use, focuses on the ratio of debt to GDP rather than the level of debt per se. The following equation captures the approach:
So the change in the debt ratio is the sum of two terms on the right-hand side: (a) the difference between the real interest rate (r) and the real GDP growth rate (g) times the initial debt ratio; and (b) the ratio of the primary deficit (G-T) to GDP.
The real interest rate is the difference between the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate. Real GDP is the nominal GDP deflated by the inflation rate. So the real GDP growth rate is equal to the Nominal GDP growth minus the inflation rate.
This standard mainstream framework is used to highlight the dangers of running deficits. But even progressives (not me) use it in a perverse way to justify deficits in a downturn balanced by surpluses in the upturn.
The question notes that “some mainstream economists” claim that a ratio of 80 per cent is a dangerous threshold that should not be passed – this is the Reinhart and Rogoff story.
Many mainstream economists and a fair number of so-called progressive economists say that governments should as some point in the business cycle run primary surpluses (taxation revenue in excess of non-interest government spending) to start reducing the debt ratio back to “safe” territory.
Almost all the media commentators that you read on this topic take it for granted that the only way to reduce the public debt ratio is to run primary surpluses. That is what the whole “credible exit strategy” hoopla is about.
Further, there is no analytical definition ever provided of what safe is and fiscal rules such as those imposed on the Eurozone nations by the Stability and Growth Pact (a maximum public debt ratio of 60 per cent) are totally arbitrary and without any foundation at all. Just numbers plucked out of the air by those who do not understand the monetary system.
MMT does not tell us that a currency-issuing government running a deficit can never reduce the debt ratio. The standard formula above can easily demonstrate that a nation running a primary deficit can reduce its public debt ratio over time.
Furthermore, depending on contributions from the external sector, a nation running a deficit will more likely create the conditions for a reduction in the public debt ratio than a nation that introduces an austerity plan aimed at running primary surpluses.
Here is why that is the case.
A growing economy can absorb more debt and keep the debt ratio constant or falling. From the formula above, if the primary budget balance is zero, public debt increases at a rate r but the public debt ratio increases at r – g.
The following Table simulates the two years in question. To make matters simple, assume a public debt ratio at the start of the Year 1 of 100 per cent (so B/Y(-1) = 1) which is equivalent to the statement that “outstanding public debt is equal to the value of the nominal GDP”.
Also the nominal interest rate is 1 per cent and the inflation rate is 1 per cent then the current real interest rate (r) is 0 per cent.
If the nominal GDP is growing at -1 per cent and there is an inflation rate of 1 per cent then real GDP is growing (g) at minus 2 per cent.
Under these conditions, the primary budget surplus would have to be equal to 2 per cent of GDP to stabilise the debt ratio (check it for yourself). So, the question suggests the primary budget deficit is actually 1 per cent of GDP we know by computation that the public debt ratio rises by 3 per cent.
The calculation (using the formula in the Table) is:
Change in B/Y = (0 – (-2))*1 + 1 = 3 per cent.
The data in Year 2 is given in the last column in the Table below. Note the public debt ratio has risen to 1.03 because of the rise from last year. You are told that the budget deficit doubles as per cent of GDP (to 2 per cent) and nominal GDP growth shoots up to 4 per cent which means real GDP growth (given the inflation rate) is equal to 3 per cent.
The corresponding calculation for the change in the public debt ratio is:
Change in B/Y = (0 – 3)*1.03 + 2 = -1.1 per cent.
So the growth in the economy is strong enough to reduce the public debt ratio even though the primary budget deficit has doubled.
It is a highly stylised example truncated into a two-period adjustment to demonstrate the point. In the real world, if the budget deficit is a large percentage of GDP then it might take some years to start reducing the public debt ratio as GDP growth ensures.
So even with an increasing (or unchanged) deficit, real GDP growth can reduce the public debt ratio, which is what has happened many times in past history following economic slowdowns.
Economists like Krugman and Mankiw argue that the government could (should) reduce the ratio by inflating it away. Noting that nominal GDP is the product of the price level (P) and real output (Y), the inflating story just increases the nominal value of output and so the denominator of the public debt ratio grows faster than the numerator.
But stimulating real growth (that is, in Y) is the other more constructive way of achieving the same relative adjustment in the denominator of the public debt ratio and its numerator.
But the best way to reduce the public debt ratio is to stop issuing debt. A sovereign government doesn’t have to issue debt if the central bank is happy to keep its target interest rate at zero or pay interest on excess reserves.
The discussion also demonstrates why tightening monetary policy makes it harder for the government to reduce the public debt ratio – which, of-course, is one of the more subtle mainstream ways to force the government to run surpluses.

Fantastic explanation to the Quantity Theory of Money and the relationship (or lack of it) between the monetary base and money supply. Great work! Thank you very much.