Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – May 3, 2014 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
As long as employment growth keeps pace with labour force growth, unemployment will not rise.
The answer is False.
If you didn’t get this correct then it is likely you lack an understanding of the labour force framework which is used by all national statistical offices.
The labour force framework is the foundation for cross-country comparisons of labour market data. The framework is made operational through the International Labour Organization (ILO) and its International Conference of Labour Statisticians (ICLS). These conferences and expert meetings develop the guidelines or norms for implementing the labour force framework and generating the national labour force data.
The rules contained within the labour force framework generally have the following features:
- an activity principle, which is used to classify the population into one of the three basic categories in the labour force framework;
- a set of priority rules, which ensure that each person is classified into only one of the three basic categories in the labour force framework; and
- a short reference period to reflect the labour supply situation at a specified moment in time.
The system of priority rules are applied such that labour force activities take precedence over non-labour force activities and working or having a job (employment) takes precedence over looking for work (unemployment). Also, as with most statistical measurements of activity, employment in the informal sectors, or black-market economy, is outside the scope of activity measures.
Paid activities take precedence over unpaid activities such that for example ‘persons who were keeping house’ as used in Australia, on an unpaid basis are classified as not in the labour force while those who receive pay for this activity are in the labour force as employed.
Similarly persons who undertake unpaid voluntary work are not in the labour force, even though their activities may be similar to those undertaken by the employed. The category of ‘permanently unable to work’ as used in Australia also means a classification as not in the labour force even though there is evidence to suggest that increasing ‘disability’ rates in some countries merely reflect an attempt to disguise the unemployment problem.
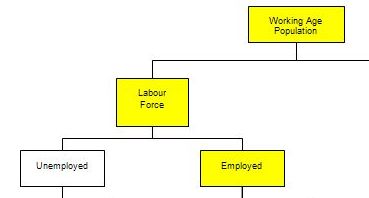
The following diagram shows a partial view of the Labour Force framework used by the statisticians in this context.
The Working Age Population (WAP) is usually defined as those persons aged between 15 and 65 years of age or increasing those persons above 15 years of age (recognising that official retirement ages are now being abandoned in many countries).
As you can see from the diagram the WAP is then split into two categories: (a) the Labour Force (LF) and; (b) Not in the Labour Force – and this division is based on activity tests (being in paid employed or actively seeking and being willing to work).
The Labour Force Participation Rate is the percentage of the WAP that are active.
You can also see that the Labour Force is divided into employment and unemployment. Most nations use the standard demarcation rule that if you have worked for one or more hours a week during the survey week you are classified as being employed.
If you are not working but indicate you are actively seeking work and are willing to currently work then you are considered to be unemployed.
If you are not working and indicate either you are not actively seeking work or are not willing to work currently then you are considered to be
Not in the Labour Force.
So you get the category of hidden unemployed who are willing to work but have given up looking because there are no jobs available. The statistician counts them as being outside the labour force even though they would accept a job immediately if offered.
Now trace through the yellow boxes which are linked by the following formulas:
Labour Force = Employment + Unemployment = Labour Force Participation Rate times the Working Age Population
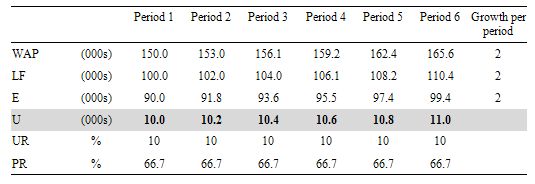
Consider the following Table which shows the Labour Force aggregates for a stylised nation and the WAP, Labour Force and Employment are all growing at a constant rate (in this case 2 per cent).
You observe unemployment rising although the unemployment rate is constant as is the participation rate.
The reason is that the Labour Force is a larger aggregate than Employment because it would be impossible for unemployment to be zero (frictions alone – people moving between jobs – will deliver some small positive unemployment).
So although both the Labour Force and Employment grow at a constant rate, the gap between them (Unemployment) gets larger each period although the proportion of the Labour Force that is unemployed remains constant.
You may wish to read the following blog for more information:
Question 2:
The non-government sector is wealthier when the government matches it deficit with new debt issues.
The answer is False.
This answer is complementary to that provided for Question 1 and relies on the same understanding of reserve operations. So within a fiat monetary system we need to understand the banking operations that occur when governments spend and issue debt. That understanding allows us to appreciate what would happen if a sovereign, currency-issuing government (with a flexible exchange rate) ran a fiscal deficit without issuing debt?
Like all government spending, the Treasury would credit the reserve accounts held by the commercial bank at the central bank. The commercial bank in question would be where the target of the spending had an account. So the commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a deposit would be made.
The transactions are clear: The commercial bank’s assets rise and its liabilities also increase because a new deposit has been made. Further, the target of the fiscal initiative enjoys increased assets (bank deposit) and net worth (a liability/equity entry on their balance sheet). Taxation does the opposite and so a deficit (spending greater than taxation) means that reserves increase and private net worth increases.
This means that there are likely to be excess reserves in the “cash system” which then raises issues for the central bank about its liquidity management as explained in the answer to Question 1. But at this stage, M1 (deposits in the non-government sector) rise as a result of the deficit without a corresponding increase in liabilities. In other words, fiscal deficits increase net financial assets in the non-government sector.
What would happen if there were bond sales? All that happens is that the banks reserves are reduced by the bond sales but this does not reduce the deposits created by the net spending. So net worth is not altered. What is changed is the composition of the asset portfolio held in the non-government sector.
The only difference between the Treasury “borrowing from the central bank” and issuing debt to the private sector is that the central bank has to use different operations to pursue its policy interest rate target. If it debt is not issued to match the deficit then it has to either pay interest on excess reserves (which most central banks are doing now anyway) or let the target rate fall to zero (the Japan solution).
There is no difference to the impact of the deficits on net worth in the non-government sector.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
- Why history matters
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- The complacent students sit and listen to some of that
- Saturday Quiz – February 27, 2010 – answers and discussion
Question 3:
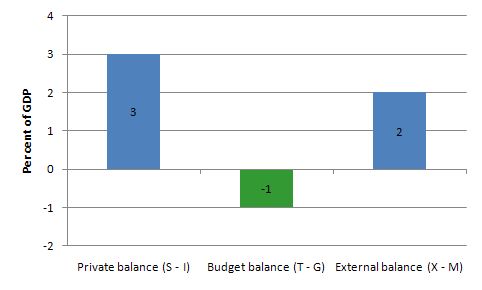
If net exports are running at 2 per cent of GDP, and the private domestic sector overall is saving an equivalent of 3 per cent of GDP, the government must:
(a) Be running a surplus equal to 1 per cent of GDP.
(b) Be running a surplus equal to 5 per cent of GDP.
(c) Be running a deficit equal to 1 per cent of GDP.
(d) Be running a deficit equal to 1 per cent of GDP.
The answer is Option C Be running a deficit equal to 1 per cent of GDP.
This question tests your knowledge of the sectoral balances that are derived from the National Accounts.
First, you need to understand the basic relationship between the sectoral flows and the balances that are derived from them. The flows are derived from the National Accounting relationship between aggregate spending and income. So:
(1) Y = C + I + G + (X – M)
where Y is GDP (income), C is consumption spending, I is investment spending, G is government spending, X is exports and M is imports (so X – M = net exports).
Another perspective on the national income accounting is to note that households can use total income (Y) for the following uses:
(2) Y = C + S + T
where S is total saving and T is total taxation (the other variables are as previously defined).
You than then bring the two perspectives together (because they are both just “views” of Y) to write:
(3) C + S + T = Y = C + I + G + (X – M)
You can then drop the C (common on both sides) and you get:
(4) S + T = I + G + (X – M)
Then you can convert this into the familiar sectoral balances accounting relations which allow us to understand the influence of fiscal policy over private sector indebtedness.
So we can re-arrange Equation (4) to get the accounting identity for the three sectoral balances – private domestic, government fiscal balance and external:
(S – I) = (G – T) + (X – M)
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)), where net exports represent the net savings of non-residents.
Another way of saying this is that total private savings (S) is equal to private investment (I) plus the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)), where net exports represent the net savings of non-residents.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
Thus, when an external deficit (X – M < 0) and public surplus (G – T < 0) coincide, there must be a private deficit. While private spending can persist for a time under these conditions using the net savings of the external sector, the private sector becomes increasingly indebted in the process.
Second, you then have to appreciate the relative sizes of these balances to answer the question correctly.
The rule is that the sectoral balances have to sum to zero. So if we write the condition above as:
(S – 1) – (G – T) – (X – M) = 0
And substitute the values of the question we get:
3 – (G – T) – 2 = 0
We can solve this for (G – T) as
(G – T) = 3 – 2 = 1
Given the construction (G – T) a positive number (1) is a deficit.
The outcome is depicted in the following graph.
This tells us that even if the external sector is growing strongly and is in surplus there may still be a need for public deficits. This will occur if the private domestic sector seek to save at a proportion of GDP higher than the external surplus.
The economics of this situation might be something like this. The external surplus would be adding to overall aggregate demand (the injection from exports exceeds the drain from imports). However, if the drain from private sector spending (S > I) is greater than the external injection then the only way output and income can remain constant is if the government is in deficit.
National income adjustments would occur if the private domestic sector tried to push for higher saving overall – income would fall (because overall spending fell) and the government would be pushed into deficit whether it liked it or not via falling revenue and rising welfare payments.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
This Post Has 0 Comments