Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – September 18, 2010 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
The stronger is the the demand for public bonds at a government auction
The answer is the lower the yields will be at that asset maturity but this tells us nothing about the effect of budget deficits on short-term interest rates
The option the lower the yields will be at that asset maturity which suggests that higher budget deficits will eventually drive short-term interest rates down might have attracted your attention given that it correctly associates higher demand for bonds will lower yields. You then may have been led by your understanding of the fundamental principles of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) that include the fact that government spending provides the net financial assets (bank reserves) and budget deficits put downward pressure on interest rates (with no accompanying central bank operations), which is contrary to the myths that appear in macroeconomic textbooks about “crowding out”.
But of-course, the central bank sets the short-term interest rate based on its policy aspirations and conducts the necessary liquidity management operations to ensure the actual short-term market interest rate is consistent with the desired policy rate. That doesn’t mean the central bank has a free rein.
It has to either offer a return on reserves equivalent to the policy rate or sell government bonds if it is to maintain a positive target rate. The “penalty for not borrowing” is that the interest rate will fall to the bottom of the “corridor” prevailing in the country which may be zero if the central bank does not offer a return on reserves.
This situation arises because the central bank essentially lacks control over the quantity of reserves in the system.
So the correct answer is that movements in public bond yields at the primary issue stage, tell us nothing about the intentions of central bank with respect to monetary policy (interest rate setting).
Given that the correct answer includes lower yields the logic developed will tell you why the option “the higher the yields will be at that asset maturity which suggests that higher budget deficits will eventually drive short-term interest rates down” was incorrect.
Why are yields inverse to price in a primary issue? The standard bond has three parameters: (a) the face value – say $A1000; (b) the coupon rate – say 5 per cent; and (c) some maturity – say 10 years. Taken together, this public debt instrument will provide the bond holder with $50 dollar per annum in interest income for 10 years whereupon they will get the $1000 face value returned.
Bonds are issued by government into the primary market, which is simply the institutional machinery via which the government sells debt to “raise funds”. In a modern monetary system with flexible exchange rates it is clear the government does not have to finance its spending so the the institutional machinery is voluntary and reflects the prevailing neo-liberal ideology – which emphasises a fear of fiscal excesses rather than any intrinsic need.
Governments are elected to advance a mandate. If that includes maximising welfare of all citizens then we should allow them to do that. If they do not perform well then we can vote them out. We do not need artificial constraints which hinder the government’s capacity to advance public purpose – these ideologically conceived restraints represent democratic repression.
Most primary market issuance is via auction. Accordingly, the government would determine the maturity of the bond (how long the bond would exist for), the coupon rate (the interest return on the bond) and the volume (how many bonds) being specified.
The issue would then be put out for tender and the market then would determine the final price of the bonds issued. Imagine a $1000 bond had a coupon of 5 per cent, meaning that you would get $50 dollar per annum until the bond matured at which time you would get $1000 back.
Imagine that the market wanted a yield of 6 per cent to accommodate risk expectations (inflation or something else). So for them the bond is unattractive and under the tender or auction system they would put in a purchase bid lower than the $1000 to ensure they get the 6 per cent return they sought.
Alternatively if the market wanted security and considered the coupon rate on offer was more than competitive then the bonds will be very attractive. Under the auction system they will bid higher than the face value up to the yields that they think are market-based. The yield reflects the last auction bid in the bond issue
The general rule for fixed-income bonds is that when the prices rise, the yield falls and vice versa. Thus, the price of a bond can change in the market place according to interest rate fluctuations.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Saturday Quiz – April 17, 2010 – answers and discussion
- Time to outlaw the credit rating agencies
- Studying macroeconomics – an exercise in deception
- Time for a reality check on debt – Part 1
- Will we really pay higher interest rates?
Question 2:
A sovereign government voluntarily issues debt to the private sector to match its spending. The more public debt it issues
The answer is the greater is non-government wealth held in the form of public debt..
The option “the less is the volume of investment funds in the non-government sector that can be used for other investments”. You may have been tempted to select this option given that the government is withdrawing bank reserves from the system. So a bond issue is a financial asset portfolio swap.
However, banks do not need deposits and reserves before they can lend. Mainstream macroeconomics wrongly asserts that banks only lend if they have prior reserves. The illusion is that a bank is an institution that accepts deposits to build up reserves and then on-lends them at a margin to make money. The conceptualisation suggests that if it doesn’t have adequate reserves then it cannot lend. So the presupposition is that by adding to bank reserves, quantitative easing will help lending.
But this is not how banks operate. Bank lending is not “reserve constrained”. Banks lend to any credit worthy customer they can find and then worry about their reserve positions afterwards. If they are short of reserves (their reserve accounts have to be in positive balance each day and in some countries central banks require certain ratios to be maintained) then they borrow from each other in the interbank market or, ultimately, they will borrow from the central bank through the so-called discount window. They are reluctant to use the latter facility because it carries a penalty (higher interest cost).
The point is that building bank reserves will not increase the bank’s capacity to lend. Loans create deposits which generate reserves. As a result, investors can always borrow if they are credit-worthy.
Further, the option “the more difficult it is for banks to attract deposits to initiate loans from” also reflects the erroneous view of the banking system.
The correct answer is based on the fact that the when the government swaps bonds for reserves (which it has itself created via its spending) it is providing the non-government sector with an interest-bearing, risk free asset (for a sovereign government) in return for a non-interest bearing reserve. Reserves may earn a return but typically have not.
The bonds are thus part of the non-government sector’s stock of wealth and the interest payments comprising a flow of income for the non-government sector. So all those national debt clocks are really just indicators of public debt wealth held by the non-government sector.
I realise some people will say that the stylisation of government funds being provided by MMT doesn’t match the institutional reality where governments is seen to borrow first and spend second. But these institutional arrangements – the democratic repression – only obscure the essence of a fiat currency system and are largely irrelevant.
If they ever created a constraint that the government didn’t wish to accept then you would see institutional change being implemented very quickly. The reality is that it is a wash – net government spending is matched by bond issuance – irrespective of these institutional procedures and the government never “needs” these funds to spend.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Quantitative easing 101
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- Money multiplier and other myths
- Will we really pay higher interest rates?
- A modern monetary theory lullaby
- Hyperdeflation, followed by rampant inflation
Question 3:
When the government pays back funds that is has borrowed from the non-government sector the payments may
The answer is be inflationary if the government payments to bond holders at maturity add more to nominal aggregate demand than the real economy can support given other policy settings..
The option “not be inflationary because the sovereign government just has to credit the bank accounts of those who hold the bonds to repay them” describes the operational reality that accompanies the repayment of the bonds and all interest payments. So in the first place, the flow of funds ends up in bank reserves.
So as it stands that option is a correct answer. But is it the best answer?
The option “be inflationary if by the time the bonds mature the economy is growing strongly so there will be too much money floating about” makes no real sense and is a typical mainstream response. What does “too much money” mean? Nothing as it stands.
The best answer is defined by the crucial assumption that is provides you with. That the funds that accompany the maturing bonds (whether they be the return of the face value or the final interest payment) are spent – that is flow into aggregate demand rather than stay suspended in bank reserves.
An increase in bank reserves is not inflationary. Outstanding public bonds do form part of the accumulated wealth of the non-government sector. At any time, they choose, non-government agents can convert the stock of wealth into a flow of spending. So the “inflation risk” inherent in the stock of financial assets is independent of maturity of the outstanding bonds.
Some might argue that the spending capacity of the private sector is not influenced by when the government repays the bonds. The argument is that the bonds by definition represent savings of the private sector which can be spent at any time regardless of the time to maturity of the outstanding financial assets
But that doesn’t negate the validity of the answer in the way I have constructed it. If non-government agents decide to run down some of their financial wealth and start spending then the inflation risk can be realised. I would stress that we should not always focus on that inflation risk as the inevitable outcome. Inflation can result when aggregate demand rises but usually will not.
In this context, it is essential to understand that the analysis of inflation is related to the state of aggregate demand relative to productive capacity.
Increased spending, in itself, is not inflationary. Nominal spending growth will stimulate real responses from firms – increased output and employment – if they have available productive capacity. Firms will be reluctant to respond to increased demand for their goods and services by increasing prices because it is expensive to do so (catalogues have to be revised etc) and they want to retain market share and fear that their competitors would not follow suit.
So generalised inflation (as opposed to price bubbles in specific asset classes) is unlikely to become an issue while there is available productive capacity.
Even at times of high demand, firms typically have some spare capacity so that they can meet demand spikes. It is only when the economy has been running at high pressure for a substantial period of time that inflationary pressures become evident and government policy to restrain demand are required (including government spending cutbacks, tax rises etc).
Further, spending growth can push the expansion of productive capacity ahead of the nominal demand growth. Investment by firms in productive capacity is an example as is government spending on productive infrastructure (including human capital development). So not all spending closes the gap between nominal spending growth and available productive capacity.
But, ultimately, if nominal demand outstrips the real capacity of the economy to respond to the spending growth then inflation is the result.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
- Will we really pay higher interest rates?
- Hyperdeflation, followed by rampant inflation
- Modern monetary theory and inflation – Part 1
Question 4:
When an external deficit and public deficit coincide, there must be a private sector deficit. This suggests that governments can only run budget deficits safely to support a private sector surplus, when net exports are strong.
The answer is False.
This question relies on your understanding of the sectoral balances that are derived from the national accounts and must hold by defintion. The statement of sectoral balances doesn’t tell us anything about how the economy might get into the situation depicted. Whatever behavioural forces were at play, the sectoral balances all have to sum to zero. Once you understand that, then deduction leads to the correct answer.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero. The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (I – S) – positive if in deficit, negative if in surplus.
- The Budget Deficit (G – T) – negative if in surplus, positive if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
A simplification is to add (I – S) + (X – M) and call it the non-government sector. Then you get the basic result that the government balance equals exactly $-for-$ (absolutely or as a per cent of GDP) the non-government balance (the sum of the private domestic and external balances).
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
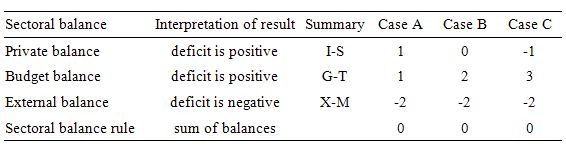
To help us answer the specific question posed, we can identify three states all involving public and external deficits:
- Case A: Budget Deficit (G – T) < Current Account balance (X – M) deficit.
- Case B: Budget Deficit (G – T) = Current Account balance (X – M) deficit.
- Case C: Budget Deficit (G – T) > Current Account balance (X – M) deficit.
The following Table shows these three cases expressing the balances as percentages of GDP. You can see that it is only in Case A when the external deficit exceeds the public deficit that the private domestic sector is in deficit.
So the answer is false because the coexistence of a budget deficit (adding to aggregate demand) and an external deficit (draining aggregate demand) does have to lead to the private domestic sector being in deficit.
With the external balance set at a 2 per cent of GDP, as the budget moves into larger deficit, the private domestic balance approaches balance (Case B). Then once the budget deficit is large enough (3 per cent of GDP) to offset the demand-draining external deficit (2 per cent of GDP) the private domestic sector can save overall (Case C).
The budget deficits are underpinning spending and allowing income growth to be sufficient to generate savings greater than investment in the private domestic sector but have to be able to offset the demand-draining impacts of the external deficits to provide sufficient income growth for the private domestic sector to save.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- Stock-flow consistent macro models
- Norway and sectoral balances
- The OECD is at it again!
- Saturday Quiz – May 22, 2010 – answers and discussion
Question 5:
When the private domestic sector decides to lift its saving ratio we cannot conclude that the national government has to increase its net spending (deficit) to avoid employment losses.
The answer is True.
The answer also relates to the sectoral balances framework developed in Question 4 and the two answers should be read as complements. When the private sector decides to lift its saving ratio, we normally think of this in terms of households reducing consumption spending. However, it could also be evidenced by a drop in investment spending (building productive capacity).
The normal inventory-cycle view of what happens next goes like this. Output and employment are functions of aggregate spending. Firms form expectations of future aggregate demand and produce accordingly. They are uncertain about the actual demand that will be realised as the output emerges from the production process.
The first signal firms get that household consumption is falling is in the unintended build-up of inventories. That signals to firms that they were overly optimistic about the level of demand in that particular period.
Once this realisation becomes consolidated, that is, firms generally realise they have over-produced, output starts to fall. Firms layoff workers and the loss of income starts to multiply as those workers reduce their spending elsewhere.
At that point, the economy is heading for a recession. Interestingly, the attempts by households overall to increase their saving ratio may be thwarted because income losses cause loss of saving in aggregate – the is the Paradox of Thrift. While one household can easily increase its saving ratio through discipline, if all households try to do that then they will fail. This is an important statement about why macroeconomics is a separate field of study.
Typically, the only way to avoid these spiralling employment losses would be for an exogenous intervention to occur – in the form of an expanding public deficit. The budget position of the government would be heading towards, into or into a larger deficit depending on the starting position as a result of the automatic stabilisers anyway.
If there are not other changes in the economy, the answer would be false. However, there is also an external sector. It is possible that at the same time that the households are reducing their consumption as an attempt to lift the saving ratio, net exports boom. A net exports boom adds to aggregate demand (the spending injection via exports is greater than the spending leakage via imports).
So it is possible that the public budget balance could actually go towards surplus and the private domestic sector increase its saving ratio if net exports were strong enough.
The important point is that the three sectors add to demand in their own ways. Total GDP and employment are dependent on aggregate demand. Variations in aggregate demand thus cause variations in output (GDP), incomes and employment. But a variation in spending in one sector can be made up via offsetting changes in the other sectors.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
So according to your explanation of question 5, we can conclude it under certain circumstances. Doesn’t that mean the answer should be Maybe?
If not, what exactly do you take Maybe to mean?
Dear Aidan
The question was:
The only correct answer is True – that is, we cannot conclude that.
If the question had have been something like “When the private domestic sector decides to lift its saving ratio the economy can avoid employment losses” or similar then Maybe would have been fine because the answer would have been based on conditions that may or may not occur but which were not specified.
best wishes
bill
Bill –
You didn’t ask whether it was sufficient to conclude that.
Anyway, a more important question:
Once this realisation becomes consolidated, that is, firms generally realise they have over-produced, output starts to fall. Firms layoff workers and the loss of income starts to multiply as those workers reduce their spending elsewhere.
What happens if the firms instead conclude they have over priced?
Q3, “When the government pays back funds that is has borrowed from the non-government sector the payments may
The answer is be inflationary if the government payments to bond holders at maturity add more to nominal aggregate demand than the real economy can support given other policy settings..”
This is exactly the point I have been trying to make. This is the rollover risk.
Q4, “So the answer is false because the coexistence of a budget deficit (adding to aggregate demand) and an external deficit (draining aggregate demand) does have to lead to the private domestic sector being in deficit.”
In case C, isn’t the private sector in surplus?