Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – October 10, 2015 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you understand the reasoning behind the answers. If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
The automatic stabilisers operate in a counter-cyclical fashion and ensure that the government fiscal balance, which rises during a recession, returns to its appropriate level once growth returns to its long-term trend.
The answer is False.
The factual statement in the proposition is that the automatic stabilisers do operate in a counter-cyclical fashion when economic growth resumes. This is because tax revenue improves given it is typically tied to income generation in some way. Further, most governments provide transfer payment relief to workers (unemployment benefits) and this increases when there is an economic slowdown.
The question is false though because this process while important may not ensure that the government fiscal balance returns to its appropriate level.
The automatic stabilisers just push the fiscal balance towards deficit, into deficit, or into a larger deficit when GDP growth declines and vice versa when GDP growth increases. These movements in aggregate demand play an important counter-cyclical attenuating role. So when GDP is declining due to falling aggregate demand, the automatic stabilisers work to add demand (falling taxes and rising welfare payments). When GDP growth is rising, the automatic stabilisers start to pull demand back as the economy adjusts (rising taxes and falling welfare payments).
We also measure the automatic stabiliser impact against some benchmark or “full capacity” or potential level of output, so that we can decompose the fiscal balance into that component which is due to specific discretionary fiscal policy choices made by the government and that which arises because the cycle takes the economy away from the potential level of output.
This decomposition provides (in modern terminology) the structural (discretionary) and cyclical fiscal balances. The fiscal components are adjusted to what they would be at the potential or full capacity level of output.
So if the economy is operating below capacity then tax revenue would be below its potential level and welfare spending would be above. In other words, the fiscal balance would be smaller at potential output relative to its current value if the economy was operating below full capacity. The adjustments would work in reverse should the economy be operating above full capacity.
If the fiscal balance is in deficit when computed at the “full employment” or potential output level, then we call this a structural deficit and it means that the overall impact of discretionary fiscal policy is expansionary irrespective of what the actual fiscal outcome is presently. If it is in surplus, then we have a structural surplus and it means that the overall impact of discretionary fiscal policy is contractionary irrespective of what the actual fiscal outcome is presently.
So you could have a downturn which drives the fiscal balance into a deficit but the underlying structural position could be contractionary (that is, a surplus). And vice versa.
The difference between the actual fiscal outcome and the structural component is then considered to be the cyclical fiscal outcome and it arises because the economy is deviating from its potential.
In some of the blogs listed below I go into the measurement issues involved in this decomposition in more detail. However for this question it these issues are less important to discuss.
The point is that structural fiscal balance has to be sufficient to ensure there is full employment. The only sensible reason for accepting the authority of a national government and ceding currency control to such an entity is that it can work for all of us to advance public purpose.
In this context, one of the most important elements of public purpose that the state has to maximise is employment. Once the private sector has made its spending (and saving decisions) based on its expectations of the future, the government has to render those private decisions consistent with the objective of full employment.
Given the non-government sector will typically desire to net save (accumulate financial assets in the currency of issue) over the course of a business cycle this means that there will be, on average, a spending gap over the course of the same cycle that can only be filled by the national government. There is no escaping that.
So then the national government has a choice – maintain full employment by ensuring there is no spending gap which means that the necessary deficit is defined by this political goal. It will be whatever is required to close the spending gap. However, it is also possible that the political goals may be to maintain some slack in the economy (persistent unemployment and underemployment) which means that the government deficit will be somewhat smaller and perhaps even, for a time, a fiscal surplus will be possible.
But the second option would introduce fiscal drag (deflationary forces) into the economy which will ultimately cause firms to reduce production and income and drive the fiscal outcome towards increasing deficits.
Ultimately, the spending gap is closed by the automatic stabilisers because falling national income ensures that that the leakages (saving, taxation and imports) equal the injections (investment, government spending and exports) so that the sectoral balances hold (being accounting constructs). But at that point, the economy will support lower employment levels and rising unemployment. The fiscal balance will also be in deficit – but in this situation, the deficits will be what I call “bad” deficits. Deficits driven by a declining economy and rising unemployment.
So fiscal sustainability requires that the government fills the spending gap with “good” deficits at levels of economic activity consistent with full employment – which I define as 2 per cent unemployment and zero underemployment.
Fiscal sustainability cannot be defined independently of full employment. Once the link between full employment and the conduct of fiscal policy is abandoned, we are effectively admitting that we do not want government to take responsibility of full employment (and the equity advantages that accompany that end).
So it will not always be the case that the dynamics of the automatic stabilisers will leave a structural deficit sufficient to finance the saving desire of the non-government sector at an output level consistent with full utilisation of resources.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- A modern monetary theory lullaby
- Saturday Quiz – April 24, 2010 – answers and discussion
- The dreaded NAIRU is still about!
- Structural deficits – the great con job!
- Structural deficits and automatic stabilisers
- Another economics department to close
Question 2:
Which scenario represents a more expansionary outcome:
(a) A fiscal deficit equivalent to 5 per cent of GDP (including the impact of automatic stabilisers equivalent to 3 per cent of GDP).
(b) A fiscal deficit equivalent to 3 per cent of GDP.
(c) You cannot tell because you do not know the decomposition between the cyclical and structural components in Option (B)
The answer is Option (a).
The question probes an understanding of the forces (components) that drive the fiscal balance that is reported by government agencies at various points in time and how to correctly interpret a fiscal balance.
In outright terms, a fiscal deficit that is equivalent to 5 per cent of GDP is more expansionary than a fiscal deficit outcome that is equivalent to 3 per cent of GDP irrespective of the cyclical and structural components.
In that sense, the question lured you into thinking that only the discretionary component (the actual policy settings) were of interest. In that context, Option (c) would have been the correct answer.
To see the why Option (a) is the best answer we have to explore the issue of decomposing the observed fiscal balance into the discretionary (now called structural) and cyclical components. The latter component is driven by the automatic stabilisers that are in-built into the fiscal process.
The federal (or national) government fiscal balance is the difference between total federal revenue and total federal outlays. So if total revenue is greater than outlays, the fiscal balance is in surplus and vice versa. It is a simple matter of accounting with no theory involved. However, the fiscal balance is used by all and sundry to indicate the fiscal stance of the government.
So if the fiscal balance is in surplus it is often concluded that the fiscal impact of government is contractionary (withdrawing net spending) and if the fiscal balance is in deficit we say the fiscal impact expansionary (adding net spending).
Further, a rising deficit (falling surplus) is often considered to be reflecting an expansionary policy stance and vice versa. What we know is that a rising deficit may, in fact, indicate a contractionary fiscal stance – which, in turn, creates such income losses that the automatic stabilisers start driving the fiscal balance back towards (or into) deficit.
So the complication is that we cannot conclude that changes in the fiscal impact reflect discretionary policy changes. The reason for this uncertainty clearly relates to the operation of the automatic stabilisers.
To see this, the most simple model of the fiscal balance we might think of can be written as:
Budget Balance = Revenue – Spending.
Budget Balance = (Tax Revenue + Other Revenue) – (Welfare Payments + Other Spending)
We know that Tax Revenue and Welfare Payments move inversely with respect to each other, with the latter rising when GDP growth falls and the former rises with GDP growth. These components of the fiscal balance are the so-called automatic stabilisers.
In other words, without any discretionary policy changes, the fiscal balance will vary over the course of the business cycle. When the economy is weak – tax revenue falls and welfare payments rise and so the fiscal balance moves towards deficit (or an increasing deficit). When the economy is stronger – tax revenue rises and welfare payments fall and the fiscal balance becomes increasingly positive. Automatic stabilisers attenuate the amplitude in the business cycle by expanding the fiscal balance in a recession and contracting it in a boom.
So just because the fiscal balance goes into deficit or the deficit increases as a proportion of GDP doesn’t allow us to conclude that the Government has suddenly become of an expansionary mind. In other words, the presence of automatic stabilisers make it hard to discern whether the fiscal policy stance (chosen by the government) is contractionary or expansionary at any particular point in time.
To overcome this uncertainty, economists devised what used to be called the Full Employment or High Employment Budget. In more recent times, this concept is now called the Structural Balance. The Full Employment Budget Balance was a hypothetical construct of the fiscal balance that would be realised if the economy was operating at potential or full employment. In other words, calibrating the fiscal position (and the underlying fiscal parameters) against some fixed point (full capacity) eliminated the cyclical component – the swings in activity around full employment.
So a full employment fiscal balance would be balanced if total outlays and total revenue were equal when the economy was operating at total capacity. If the fiscal balance was in surplus at full capacity, then we would conclude that the discretionary structure of the fiscal balance was contractionary and vice versa if the fiscal balance was in deficit at full capacity.
The calculation of the structural deficit spawned a bit of an industry in the past with lots of complex issues relating to adjustments for inflation, terms of trade effects, changes in interest rates and more.
Much of the debate centred on how to compute the unobserved full employment point in the economy. There were a plethora of methods used in the period of true full employment in the 1960s. All of them had issues but like all empirical work – it was a dirty science – relying on assumptions and simplifications. But that is the nature of the applied economist’s life.
As I explain in the blogs cited below, the measurement issues have a long history and current techniques and frameworks based on the concept of the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (the NAIRU) bias the resulting analysis such that actual discretionary positions which are contractionary are seen as being less so and expansionary positions are seen as being more expansionary.
The result is that modern depictions of the structural deficit systematically understate the degree of discretionary contraction coming from fiscal policy.
So the data provided by the question unambiguously points to Option (a) being the more expansionary impact – made up of a discretionary (structural) deficit of 2 per cent and a cyclical impact of 3 per cent. The cyclical impact is still expansionary – lower tax revenue and higher welfare payments.
Option (b) might in fact signal a higher structural deficit which would indicate a more expansionary fiscal intent from government but it could also indicate a large automatic stabiliser (cyclical) component.
You might like to read these blogs for further information:
Question 3:
If private domestic investment is less than private domestic saving and the current account is in deficit then the government fiscal balance will be in deficit no matter what growth rate GDP is generated.
The answer is True.
This question requires an understanding of the sectoral balances that can be derived from the National Accounts. But it also requires some understanding of the behavioural relationships within and between these sectors which generate the outcomes that are captured in the National Accounts and summarised by the sectoral balances.
Refreshing the balances (again) – we know that from an accounting sense, if the external sector overall is in deficit, then it is impossible for both the private domestic sector and government sector to run surpluses. One of those two has to also be in deficit to satisfy the accounting rules.
The important point is to understand what behaviour and economic adjustments drive these outcomes.
So here is the accounting (again). The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero. The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (I – S) – positive if in deficit, negative if in surplus.
- The Budget Deficit (G – T) – negative if in surplus, positive if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
A simplification is to add (I – S) + (X – M) and call it the non-government sector. Then you get the basic result that the government balance equals exactly $-for-$ (absolutely or as a per cent of GDP) the non-government balance (the sum of the private domestic and external balances).
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
So what about the situation posed in the question?
If the external sector is draining aggregate demand it must mean the current account is in deficit. That is , spending flows out of the local economy are greater than spending flows coming into the economy from the foreign sector.
If private domestic investment is less than private domestic saving, then the private domestic sector is running a surplus overall – that is, they are spending less than they are earning.
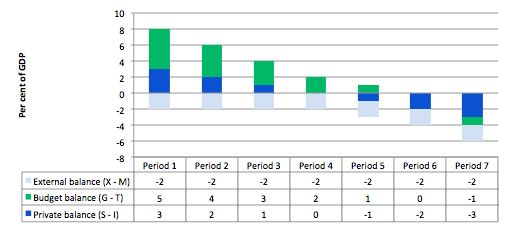
The following graph shows the sectoral balances for seven periods based on different levels of the private balance (as a per cent of GDP) and a constant external deficit (to keep things simple).
You can see that in Periods 1 to 3, the private sector is in surplus while the external sector is in deficit. The fiscal balance (G – T) is in deficit in each of those periods. The fiscal balance only goes into surplus (with a 2 per cent of GDP external deficit) when the injection into aggregate demand from the private domestic sector is greater than the spending drain from the external sector (Period 7).
The reasoning is as follows. If the private domestic sector (households and firms) is saving overall it means that some of the income being produced is not be re-spent. So the private domestic surplus represents a drain on aggregate demand. The external sector is also leaking expenditure. At the current GDP level, if the government didn’t fill the spending gap resulting from the other sectors, then inventories would start to increase beyond the desired level of the firms.
The firms would react to the increased inventory holding costs and would cut back production. How quickly this downturn occurs would depend on a number of factors including the pace and magnitude of the initial demand contraction. But the result would be that the economy would contract – output, employment and income would all fall.
The initial contraction in consumption would multiply through the expenditure system as laid-off workers lose income and cut back on their spending. This would lead to further contractions.
Declining national income (GDP) leads to a number of consequences. Net exports improve as imports fall (less income) but the question clearly assumes that the external sector remains in deficit. Total saving actually starts to decline as income falls as does induced consumption.
The decline in income then stifles firms’ investment plans – they become pessimistic of the chances of realising the output derived from augmented capacity and so aggregate demand plunges further. Both these effects push the private domestic balance further into surplus
With the economy in decline, tax revenue falls and welfare payments rise which push the public fiscal balance towards and eventually into deficit via the automatic stabilisers.
So with an external deficit and a private domestic surplus there will always be a fiscal deficit.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
Re: Q3
“If private domestic investment is less than private domestic saving and the current account is in deficit then the government fiscal balance will be in deficit no matter what growth rate GDP is generated.”
But what about private consumption spending?