Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
Saturday Quiz – June 22, 2013 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for yesterday’s quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of modern monetary theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
If workers (on average across the economy) suffer real wage losses because their nominal wages fail to keep pace with the inflation rate then a greater share of national income is going to profits.
The answer is False.
The wage share in nominal GDP is expressed as the total wage bill as a percentage of nominal GDP. Economists differentiate between nominal GDP ($GDP), which is total output produced at market prices and real GDP (GDP), which is the actual physical equivalent of the nominal GDP. We will come back to that distinction soon.
To compute the wage share we need to consider total labour costs in production and the flow of production ($GDP) each period.
Employment (L) is a stock and is measured in persons (averaged over some period like a month or a quarter or a year.
The wage bill is a flow and is the product of total employment (L) and the average nominal wage (w) prevailing at any point in time. Stocks (L) become flows if it is multiplied by a flow variable (W). So the wage bill is the total labour costs in production per period.
So the wage bill = W.L
The wage share is just the total labour costs expressed as a proportion of $GDP – (W.L)/$GDP in nominal terms, usually expressed as a percentage. We can actually break this down further.
Labour productivity (LP) is the units of real GDP per person employed per period. Using the symbols already defined this can be written as:
LP = GDP/L
so it tells us what real output (GDP) each labour unit that is added to production produces on average.
We can also define another term that is regularly used in the media – the real wage – which is the purchasing power equivalent on the nominal wage that workers get paid each period. To compute the real wage we need to consider two variables: (a) the nominal wage (W) and the aggregate price level (P).
We might consider the aggregate price level to be measured by the consumer price index (CPI) although there are huge debates about that. But in a sense, this macroeconomic price level doesn’t exist but represents some abstract measure of the general movement in all prices in the economy.
Macroeconomics is hard to learn because it involves these abstract variables that are never observed – like the price level, like “the interest rate” etc. They are just stylisations of the general tendency of all the different prices and interest rates.
Now the nominal wage (W) – that is paid by employers to workers is determined in the labour market – by the contract of employment between the worker and the employer. The price level (P) is determined in the goods market – by the interaction of total supply of output and aggregate demand for that output although there are complex models of firm price setting that use cost-plus mark-up formulas with demand just determining volume sold. We shouldn’t get into those debates here.
The inflation rate is just the continuous growth in the price level (P). A once-off adjustment in the price level is not considered by economists to constitute inflation.
So the real wage (w) tells us what volume of real goods and services the nominal wage (W) will be able to command and is obviously influenced by the level of W and the price level. For a given W, the lower is P the greater the purchasing power of the nominal wage and so the higher is the real wage (w).
We write the real wage (w) as W/P. So if W = 10 and P = 1, then the real wage (w) = 10 meaning that the current wage will buy 10 units of real output. If P rose to 2 then w = 5, meaning the real wage was now cut by one-half.
Nominal GDP ($GDP) can be written as P.GDP, where the P values the real physical output.
Now if you put of these concepts together you get an interesting framework. To help you follow the logic here are the terms developed and be careful not to confuse $GDP (nominal) with GDP (real):
- Wage share = (W.L)/$GDP
- Nominal GDP: $GDP = P.GDP
- Labour productivity: LP = GDP/L
- Real wage: w = W/P
By substituting the expression for Nominal GDP into the wage share measure we get:
Wage share = (W.L)/P.GDP
In this area of economics, we often look for alternative way to write this expression – it maintains the equivalence (that is, obeys all the rules of algebra) but presents the expression (in this case the wage share) in a different “view”.
So we can write as an equivalent:
Wage share = (W/P).(L/GDP)
Now if you note that (L/GDP) is the inverse (reciprocal) of the labour productivity term (GDP/L). We can use another rule of algebra (reversing the invert and multiply rule) to rewrite this expression again in a more interpretable fashion.
So an equivalent but more convenient measure of the wage share is:
Wage share = (W/P)/(GDP/L) – that is, the real wage (W/P) divided by labour productivity (GDP/L).
I won’t show this but I could also express this in growth terms such that if the growth in the real wage equals labour productivity growth the wage share is constant. The algebra is simple but we have done enough of that already.
That journey might have seemed difficult to non-economists (or those not well-versed in algebra) but it produces a very easy to understand formula for the wage share.
Two other points to note. The wage share is also equivalent to the real unit labour cost (RULC) measures that Treasuries and central banks use to describe trends in costs within the economy. Please read my blog – Saturday Quiz – May 15, 2010 – answers and discussion – for more discussion on this point.
Now it becomes obvious that if the nominal wage (W) and the price level (P) are growing at the pace the real wage is constant. And if the real wage is growing at the same rate as labour productivity, then both terms in the wage share ratio are equal and so the wage share is constant.
However, if the real wage is falling we cannot conclude that the wage share is also falling. Given the nature of ratios, if the numerator (in this case, the real wage) is falling but not by as much as the denominator (in this case, labour productivity) then the overall ratio can actually be rising.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
- The origins of the economic crisis
- The fiscal stimulus worked but was captured by profits
- When will the workers wake up?
Question 2:
The wider the spread between the price the central bank sets on the reserves it provides the commercial banks on demand (so-called penalty rates) and the target policy rate the more difficult it becomes for the central bank to ensure the quantity of reserves is appropriate for maintaining its target policy rate.
The answer is True.
The facts are as follows. First, central banks will always provided enough reserve balances to the commercial banks at a price it sets using a combination of overdraft/discounting facilities and open market operations.
Second, if the central bank didn’t provide the reserves necessary to match the growth in deposits in the commercial banking system then the payments system would grind to a halt and there would be significant hikes in the interbank rate of interest and a wedge between it and the policy (target) rate – meaning the central bank’s policy stance becomes compromised.
Third, any reserve requirements within this context while legally enforceable (via fines etc) do not constrain the commercial bank credit creation capacity. Central bank reserves (the accounts the commercial banks keep with the central bank) are not used to make loans. They only function to facilitate the payments system (apart from satisfying any reserve requirements).
Fourth, banks make loans to credit-worthy borrowers and these loans create deposits. If the commercial bank in question is unable to get the reserves necessary to meet the requirements from other sources (other banks) then the central bank has to provide them. But the process of gaining the necessary reserves is a separate and subsequent bank operation to the deposit creation (via the loan).
Fifth, if there were too many reserves in the system (relative to the banks’ desired levels to facilitate the payments system and the required reserves then competition in the interbank (overnight) market would drive the interest rate down. This competition would be driven by banks holding surplus reserves (to their requirements) trying to lend them overnight. The opposite would happen if there were too few reserves supplied by the central bank. Then the chase for overnight funds would drive rates up.
In both cases the central bank would lose control of its current policy rate as the divergence between it and the interbank rate widened. This divergence can snake between the rate that the central bank pays on excess reserves (this rate varies between countries and overtime but before the crisis was zero in Japan and the US) and the penalty rate that the central bank seeks for providing the commercial banks access to the overdraft/discount facility.
So the aim of the central bank is to issue just as many reserves that are required for the law and the banks’ own desires.
Now the question seeks to link the penalty rate that the central bank charges for providing reserves to the banks and the central bank’s target rate. The wider the spread between these rates the more difficult does it become for the central bank to ensure the quantity of reserves is appropriate for maintaining its target (policy) rate.
Where this spread is narrow, central banks “hit” their target rate each day more precisely than when the spread is wider.
So if the central bank really wanted to put the screws on commercial bank lending via increasing the penalty rate, it would have to be prepared to lift its target rate in close correspondence. In other words, its monetary policy stance becomes beholden to the discount window settings.
The answer is True because the central bank cannot operate with wide divergences between the penalty rate and the target rate and it is likely that the former would have to rise significantly to choke private bank credit creation.
You might like to read this blog for further information:
- US federal reserve governor is part of the problem
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
Question 3:
Assume that a national is continuously running an external surplus of 1 per cent of GDP. This surplus provides the scope for the government to run a equivalent surplus and still satisfy a desire by the private domestic to save overall.
The answer is False.
This question requires an understanding of the sectoral balances that can be derived from the National Accounts. But it also requires some understanding of the behavioural relationships within and between these sectors which generate the outcomes that are captured in the National Accounts and summarised by the sectoral balances.
Refreshing the balances (again) – we know that from an accounting sense, if the external sector overall is in deficit, then it is impossible for both the private domestic sector and government sector to run surpluses. One of those two has to also be in deficit to satisfy the accounting rules.
The important point is to understand what behaviour and economic adjustments drive these outcomes.
So here is the accounting (again). The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X – M).
From the uses perspective, national income (GDP) can be used for:
GDP = C + S + T
which says that GDP (income) ultimately comes back to households who consume (C), save (S) or pay taxes (T) with it once all the distributions are made.
Equating these two perspectives we get:
C + S + T = GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
So after simplification (but obeying the equation) we get the sectoral balances view of the national accounts.
(I – S) + (G – T) + (X – M) = 0
That is the three balances have to sum to zero. The sectoral balances derived are:
- The private domestic balance (I – S) – positive if in deficit, negative if in surplus.
- The Budget Deficit (G – T) – negative if in surplus, positive if in deficit.
- The Current Account balance (X – M) – positive if in surplus, negative if in deficit.
These balances are usually expressed as a per cent of GDP but that doesn’t alter the accounting rules that they sum to zero, it just means the balance to GDP ratios sum to zero.
A simplification is to add (I – S) + (X – M) and call it the non-government sector. Then you get the basic result that the government balance equals exactly $-for-$ (absolutely or as a per cent of GDP) the non-government balance (the sum of the private domestic and external balances).
This is also a basic rule derived from the national accounts and has to apply at all times.
So what economic behaviour might lead to the outcome specified in the question?
If the nation is running an external surplus it means that the contribution to aggregate demand from the external sector is positive – that is adding to spending on domestically produced goods and services.
So if the budget was in balance – neither adding or subtracting from aggregate demand, the external surplus would provide sufficient demand for the private domestic sector to save overall equivalent to 1 per cent of GDP.
Assume, now that the private domestic sector (households and firms) desires to save overall more than 1 per cent of GDP. Consistent with this aspiration, households may cut back on consumption spending and save more out of disposable income. The immediate impact is that aggregate demand will fall and inventories will start to increase beyond the desired level of the firms.
The firms will soon react to the increased inventory holding costs and will start to cut back production. How quickly this happens depends on a number of factors including the pace and magnitude of the initial demand contraction. But if the households persist in trying to save more and consumption continues to lag, then soon enough the economy starts to contract – output, employment and income all fall.
The initial contraction in consumption multiplies through the expenditure system as workers who are laid off also lose income and their spending declines. This leads to further contractions.
The declining income leads to a number of consequences. Net exports improve as imports fall (less income) but the question clearly assumes that the external sector remains in deficit. Total saving actually starts to decline as income falls as does induced consumption.
So the initial discretionary decline in consumption is supplemented by the induced consumption falls driven by the multiplier process.
The decline in income then stifles firms’ investment plans – they become pessimistic of the chances of realising the output derived from augmented capacity and so aggregate demand plunges further. Both these effects push the private domestic balance further towards and eventually into surplus
With the economy in decline, tax revenue falls and welfare payments rise which would in this instance push the public budget balance into deficit via the automatic stabilisers if there were no discretionary policy changes made by government.
If the private sector persists in trying to increase its overall saving then the contracting income will clearly push the budget into a larger deficit.
So if there is an external surplus and the private domestic sector saves overall (a surplus) then the budget surplus has to be lower than the external surplus. If the government tried to run a surplus greater than the external surplus then then the net drain on aggregate demand would reduce national income and saving for given investment levels and drive the private domestic sector into deficit.
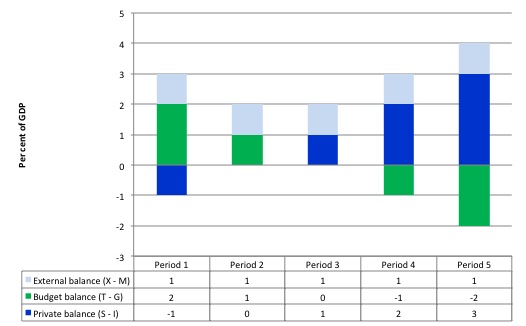
The following graph and related data table shows you the sectoral balances written as (G-T) = (S-I) – (X-M) and how a budget surplus equivalent to the external surplus will not permit the private domestic sector to save overall.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you:
With regard to the real wage question, it’s worth noting that the P used for determining the real wage should not be the same as the P implied in nominal GDP. The former would typically be some index of consumer prices, whilst the latter should be the GDP deflator. There are various reasons why these might diverge, but the most important to be aware of is changes in import prices, for example due to exchange rate movements. In particular, a rise in import prices will directly increase consumer prices but not the GDP deflator, potentially leading to a real wage reduction without any impact on the profit share.