Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern…
The Weekend Quiz – September 4-5, 2021 – answers and discussion
Here are the answers with discussion for this Weekend’s Quiz. The information provided should help you work out why you missed a question or three! If you haven’t already done the Quiz from yesterday then have a go at it before you read the answers. I hope this helps you develop an understanding of Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and its application to macroeconomic thinking. Comments as usual welcome, especially if I have made an error.
Question 1:
MMT recognises that increasing the amount of money in the economy will reduce its value.
The answer is Maybe.
The question is mostly false but there are situations (rare) where it could be true – so maybe.
The question requires you to: (a) understand the difference between bank reserves and the money supply; and (b) understand the Quantity Theory of Money.
The mainstream macroeconomics text book argument that increasing the money supply will cause inflation is based on the Quantity Theory of Money. First, expanding bank reserves will put more base money into the economy but not increase the aggregates that drive the alleged causality in the Quantity Theory of Money – that is, the various estimates of the “money supply”.
Second, even if the money supply is increasing, the economy may still adjust to that via output and income increases up to full capacity. Over time, as investment expands the productive capacity of the economy, aggregate demand growth can support the utilisation of that increased capacity without there being inflation.
In this situation, an increasing money supply (which is really not a very useful aggregate at all) which signals expanding credit will not be inflationary.
So the Maybe relates to the situation that might arise if nominal demand kept increasing beyond the capacity of the real economy to absorb it via increased production. Then you would get inflation and the “value” of the dollar would start to decline.
The Quantity Theory of Money which in symbols is MV = PQ but means that the money stock times the turnover per period (V) is equal to the price level (P) times real output (Q). The mainstream assume that V is fixed (despite empirically it moving all over the place) and Q is always at full employment as a result of market adjustments.
In applying this theory the mainstream deny the existence of unemployment. The more reasonable mainstream economists admit that short-run deviations in the predictions of the Quantity Theory of Money can occur but in the long-run all the frictions causing unemployment will disappear and the theory will apply.
In general, the Monetarists (the most recent group to revive the Quantity Theory of Money) claim that with V and Q fixed, then changes in M cause changes in P – which is the basic Monetarist claim that expanding the money supply is inflationary. They say that excess monetary growth creates a situation where too much money is chasing too few goods and the only adjustment that is possible is nominal (that is, inflation).
One of the contributions of Keynes was to show the Quantity Theory of Money could not be correct. He observed price level changes independent of monetary supply movements (and vice versa) which changed his own perception of the way the monetary system operated.
Further, with high rates of capacity and labour underutilisation at various times (including now) one can hardly seriously maintain the view that Q is fixed. There is always scope for real adjustments (that is, increasing output) to match nominal growth in aggregate demand. So if increased credit became available and borrowers used the deposits that were created by the loans to purchase goods and services, it is likely that firms with excess capacity will react to the increased nominal demand by increasing output.
The mainstream have related the current non-standard monetary policy efforts – the so-called quantitative easing – to the Quantity Theory of Money and predicted hyperinflation will arise.
So it is the modern belief in the Quantity Theory of Money is behind the hysteria about the level of bank reserves at present – it has to be inflationary they say because there is all this money lying around and it will flood the economy.
Textbook like that of Mankiw mislead their students into thinking that there is a direct relationship between the monetary base and the money supply. They claim that the central bank “controls the money supply by buying and selling government bonds in open-market operations” and that the private banks then create multiples of the base via credit-creation.
Students are familiar with the erroneous concept of the money multiplier where a banks are alleged to “loan out some of its reserves and create money”. As I have indicated several times the depiction of the fractional reserve-money multiplier process in textbooks like Mankiw exemplifies the mainstream misunderstanding of banking operations.
Please read my blog – Money multiplier and other myths – for more discussion on this point.
The idea that the monetary base (the sum of bank reserves and currency) leads to a change in the money supply via some multiple is not a valid representation of the way the monetary system operates even though it appears in all mainstream macroeconomics textbooks and is relentlessly rammed down the throats of unsuspecting economic students.
The money multiplier myth leads students to think that as the central bank can control the monetary base then it can control the money supply. Further, given that inflation is allegedly the result of the money supply growing too fast then the blame is sheeted home to the “government” (the central bank in this case).
The reality is that the central bank does not have the capacity to control the money supply. We have regularly traversed this point. In the world we live in, bank loans create deposits and are made without reference to the reserve positions of the banks. The bank then ensures its reserve positions are legally compliant as a separate process knowing that it can always get the reserves from the central bank.
The only way that the central bank can influence credit creation in this setting is via the price of the reserves it provides on demand to the commercial banks.
So when we talk about quantitative easing, we must first understand that it requires the short-term interest rate to be at zero or close to it. Otherwise, the central bank would not be able to maintain control of a positive interest rate target because the excess reserves would invoke a competitive process in the interbank market which would effectively drive the interest rate down.
Quantitative easing then involves the central bank buying assets from the private sector – government bonds and high quality corporate debt. So what the central bank is doing is swapping financial assets with the banks – they sell their financial assets and receive back in return extra reserves. So the central bank is buying one type of financial asset (private holdings of bonds, company paper) and exchanging it for another (reserve balances at the central bank). The net financial assets in the private sector are in fact unchanged although the portfolio composition of those assets is altered (maturity substitution) which changes yields and returns.
In terms of changing portfolio compositions, quantitative easing increases central bank demand for “long maturity” assets held in the private sector which reduces interest rates at the longer end of the yield curve. These are traditionally thought of as the investment rates. This might increase aggregate demand given the cost of investment funds is likely to drop. But on the other hand, the lower rates reduce the interest-income of savers who will reduce consumption (demand) accordingly.
How these opposing effects balance out is unclear but the evidence suggests there is not very much impact at all.
For the monetary aggregates (outside of base money) to increase, the banks would then have to increase their lending and create deposits. This is at the heart of the mainstream belief is that quantitative easing will stimulate the economy sufficiently to put a brake on the downward spiral of lost production and the increasing unemployment. The recent experience (and that of Japan in 2001) showed that quantitative easing does not succeed in doing this.
This should come as no surprise at all if you understand Modern Monetary Theory (MMT).
The mainstream view is based on the erroneous belief that the banks need reserves before they can lend and that quantitative easing provides those reserves. That is a major misrepresentation of the way the banking system actually operates. But the mainstream position asserts (wrongly) that banks only lend if they have prior reserves.
The illusion is that a bank is an institution that accepts deposits to build up reserves and then on-lends them at a margin to make money. The conceptualisation suggests that if it doesn’t have adequate reserves then it cannot lend. So the presupposition is that by adding to bank reserves, quantitative easing will help lending.
But banks do not operate like this. Bank lending is not “reserve constrained”. Banks lend to any credit worthy customer they can find and then worry about their reserve positions afterwards. If they are short of reserves (their reserve accounts have to be in positive balance each day and in some countries central banks require certain ratios to be maintained) then they borrow from each other in the interbank market or, ultimately, they will borrow from the central bank through the so-called discount window. They are reluctant to use the latter facility because it carries a penalty (higher interest cost).
The point is that building bank reserves will not increase the bank’s capacity to lend. Loans create deposits which generate reserves.
The reason that the commercial banks are currently not lending much is because they are not convinced there are credit worthy customers on their doorstep. In the current climate the assessment of what is credit worthy has become very strict compared to the lax days as the top of the boom approached.
Those that claim that quantitative easing will expose the economy to uncontrollable inflation are just harking back to the old and flawed Quantity Theory of Money. This theory has no application in a modern monetary economy and proponents of it have to explain why economies with huge excess capacity to produce (idle capital and high proportions of unused labour) cannot expand production when the orders for goods and services increase. Should quantitative easing actually stimulate spending then the depressed economies will likely respond by increasing output not prices.
So the fact that large scale quantitative easing conducted by central banks in Japan in 2001 and now in the UK and the USA has not caused inflation does not provide a strong refutation of the mainstream Quantity Theory of Money because it has not impacted on the monetary aggregates.
The fact that is hasn’t is not surprising if you understand how the monetary system operates but it has certainly bedazzled the (easily dazzled) mainstream economists.
The following blog posts may be of further interest to you:
- Money multiplier and other myths
- Islands in the sun
- Operation twist – then and now
- Quantitative easing 101
- Building bank reserves will not expand credit
- Building bank reserves is not inflationary
Question 2:
If national government public works expenditure funds the construction of a new road but then digs it up and rebuilds, the expenditure in the rebuild would not count towards national income.
The answer is False.
This question allows us to go back into J.M. Keynes’ The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money. Many mainstream economics characterise the Keynesian position on the use of public works as an expansionary employment measure as advocating useless work – digging holes and filling them up again. The critics focus on the seeming futility of that work to denigrate it and rarely examine the flow of funds and impacts on aggregate demand. They know that people will instinctively recoil from the idea if the nonsensical nature of the work is emphasised.
The critics actually fail in their stylisations of what Keynes actually said. They also fail to understand the nature of the policy recommendations that Keynes was advocating.
What Keynes demonstrated was that when private demand fails during a recession and the private sector will not buy any more goods and services, then government spending interventions were necessary. He said that while hiring people to dig holes only to fill them up again would work to stimulate demand, there were much more creative and useful things that the government could do.
Keynes maintained that in a crisis caused by inadequate private willingness or ability to buy goods and services, it was the role of government to generate demand. But, he argued, merely hiring people to dig holes, while better than nothing, is not a reasonable way to do it.
In Chapter 16 of The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, Keynes wrote, in the book’s typically impenetrable style:
If — for whatever reason — the rate of interest cannot fall as fast as the marginal efficiency of capital would fall with a rate of accumulation corresponding to what the community would choose to save at a rate of interest equal to the marginal efficiency of capital in conditions of full employment, then even a diversion of the desire to hold wealth towards assets, which will in fact yield no economic fruits whatever, will increase economic well-being. In so far as millionaires find their satisfaction in building mighty mansions to contain their bodies when alive and pyramids to shelter them after death, or, repenting of their sins, erect cathedrals and endow monasteries or foreign missions, the day when abundance of capital will interfere with abundance of output may be postponed. “To dig holes in the ground,” paid for out of savings, will increase, not only employment, but the real national dividend of useful goods and services. It is not reasonable, however, that a sensible community should be content to remain dependent on such fortuitous and often wasteful mitigations when once we understand the influences upon which effective demand depends.
So while the narrative style is typical Keynes (I actually think the General Theory is a poorly written book) the message is clear. Keynes clearly understands that digging holes will stimulate aggregate demand when private investment has fallen but not increase “the real national dividend of useful goods and services”.
He also notes that once the public realise how employment is determined and the role that government can play in times of crisis they would expect government to use their net spending wisely to create useful outcomes.
Earlier, in Chapter 10 of the General Theory you read the following:
If the Treasury were to fill old bottles with banknotes, bury them at suitable depths in disused coalmines which are then filled up to the surface with town rubbish, and leave it to private enterprise on well-tried principles of laissez-faire to dig the notes up again (the right to do so being obtained, of course, by tendering for leases of the note-bearing territory), there need be no more unemployment and, with the help of the repercussions, the real income of the community, and its capital wealth also, would probably become a good deal greater than it actually is. It would, indeed, be more sensible to build houses and the like; but if there are political and practical difficulties in the way of this, the above would be better than nothing.
Again a similar theme. The government can stimulate demand in a number of ways when private spending collapses. But they should choose ways that will yield more “sensible” products such as housing. He notes too that politics might intervene in doing what is best. When that happens the sub-optimal but effective outcome would be suitable.
So the answer is false. As long as the road builder is paying on-going wages to construct, tear up and construct the road again then this will be beneficial for aggregate demand. The workers employed will spend a proportion of their weekly incomes on other goods and services which, in turn, provides wages to workers providing those outputs. They spend a proportion of this income and the “induced consumption” (induced from the initial spending on the road) multiplies throughout the economy.
This is the idea behind the expenditure multiplier.
The economy may not get much useful output from such a policy but aggregate demand would be higher as a consequence.
The following blog posts may be of further interest to you:
Question 3:
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the extra consumption that is induced for every extra dollar of national income. The marginal propensity to import (MPM) is similarly the extra spending on imports that is induced for every extra dollar of national income. If the MPC and MPM both rise by 0.1 then the impact on aggregate demand for every new dollar of national income generated will be neutral.
The answer is False.
When there is an externally-motivated source of increased aggregate spending (say an injection of government spending or an autonomous increase in private investment), the economy will typically respond by increasing production which generates an equivalent increase in income. This situation relies on their being idle resources than can be brought into the production process and does not apply at full capacity.
So what is spent will generate income in that period which is available for use. The uses are further consumption; paying taxes and/or buying imports. We consider imports as a separate category (even though they reflect consumption, investment and government spending decisions) because they constitute spending which does not recycle back into the production process. They are thus considered to be “leakages” from the expenditure system.
So if for every dollar produced and paid out as income, if the economy imports around 20 cents in the dollar, then only 80 cents is available within the system for spending in subsequent periods excluding taxation considerations. We call this reaction the marginal propensity to import (MPM).
However there are two other “leakages” which arise from domestic sources – saving and taxation. Take taxation first. When income is produced, the households end up with less than they are paid out in gross terms because the government levies a tax. So the income concept available for subsequent spending is called disposable income (Yd).
To keep it simple, imagine a proportional tax of 20 cents in the dollar is levied, so if $100 of income is generated, $20 goes to taxation and Yd is $80 (what is left). So taxation (T) is a “leakage” from the expenditure system in the same way as imports are.
Finally consider saving. Consumers make decisions to spend a proportion of their disposable income. The amount of each dollar they spent at the margin (that is, how much of every extra dollar to they consume) is called the marginal propensity to consume (MPC). If that is 0.80 then they spent 80 cents in every dollar of disposable income.
So if total disposable income is $80 (after taxation of 20 cents in the dollar is collected) then consumption (C) will be 0.80 times $80 which is $64 and saving will be the residual – $16. Saving (S) is also a “leakage” from the expenditure system.
It is easy to see that for every $100 produced, the income that is generated and distributed results in $64 in consumption and $36 in leakages which do not cycle back into spending.
For income to remain at $100 in the next period the $36 has to be made up by what economists call “injections” which in these sorts of models comprise the sum of investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X). The injections are seen as coming from “outside” the output-income generating process (they are called exogenous or autonomous expenditure variables).
Investment is dependent on expectations of future revenue and costs of borrowing. Government spending is clearly a reflection of policy choices available to government. Exports are determined by world incomes and real exchange rates etc.
For GDP to be stable injections have to equal leakages (this can be converted into growth terms to the same effect). The national accounting statements that we have discussed previous such that the government deficit (surplus) equals $-for-$ the non-government surplus (deficit) and those that decompose the non-government sector in the external and private domestic sectors is derived from these relationships.
So imagine there is a certain level of income being produced – its value is immaterial. Imagine that the central bank sees no inflation risk and so interest rates are stable as are exchange rates (these simplifications are to to eliminate unnecessary complexity).
The question then is: what would happen if government increased spending by, say, $100? In macroeconomics this question is answered by examining what it known as the expenditure multiplier. If aggregate demand increases drive higher output and income increases then the question is by how much?
The expenditure multiplier is defined as the change in real income that results from a dollar change in exogenous aggregate demand (so one of G, I or X). We could complicate this by having autonomous consumption as well but the principle is not altered.
Consumption and Saving
So the starting point is to define the consumption relationship. The most simple is a proportional relationship to disposable income (Yd). So we might write it as C = c*Yd – where little c is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) or the fraction of every dollar of disposable income consumed. We will use c = 0.8.
The * sign denotes multiplication. You can do this example in an spreadsheet if you like.
Taxes
Our tax relationship is already defined above – so T = tY. The little t is the marginal tax rate which in this case is the proportional rate (assume it is 0.2). Note here taxes are taken out of total income (Y) which then defines disposable income.
So Yd = (1-t) times Y or Yd = (1-0.2)*Y = 0.8*Y
Imports
If imports (M) are 20 per cent of total income (Y) then the relationship is M = m*Y where little m is the marginal propensity to import or the economy will increase imports by 20 cents for every real GDP dollar produced.
Multiplier
If you understand all that then the explanation of the multiplier follows logically. Imagine that government spending went up by $100 and the change in real national income is $179. Then the multiplier is the ratio (denoted k) of the Change in Total Income to the Change in government spending.
Thus k = $179/$100 = 1.79.
This says that for every dollar the government spends total real GDP will rise by $1.79 after taking into account the leakages from taxation, saving and imports.
When we conduct this thought experiment we are assuming the other autonomous expenditure components (I and X) are unchanged.
But the important point is to understand why the process generates a multiplier value of 1.79.
The formula for the spending multiplier is given as:
k = 1/(1 – c*(1-t) + m)
where c is the MPC, t is the tax rate so c(1-t) is the extra spending per dollar of disposable income and m is the MPM. The * denotes multiplication as before.
This formula is derived as follows:
The national income identity outlined in Question 4 is:
GDP = Y = C + I + G + (X – M)
A simple model of these expenditure components taking the information above is:
GDP = Y = c*Yd + I + G + X – m*Y
Yd = (1 – t)*Y
We consider (in this model for simplicity) that the expenditure components I, G and X are autonomous and do not depend on the level of income (GDP) in any particular period. So we can aggregate them as all autonomous expenditure A.
Thus:
GDP = Y = c*(1- t)*Y -m*Y + A
While I am not trying to test one’s ability to do algebra, and in that sense the answer can be worked out conceptually, to get the multiplier formula we re-arrange the previous equation as follows:
Y – c*(1-t)*Y + m*Y = A
Then collect the like terms and simplify:
Y[1-c*(1-t) + m] = A
So a change in A will generate a change in Y according to the this formula:
Change in Y = k = 1/(1 -c*(1-t) + m)*Change in A
or if k = 1/(1 -c*(1-t) + m)
Change in Y = k*Change in A.
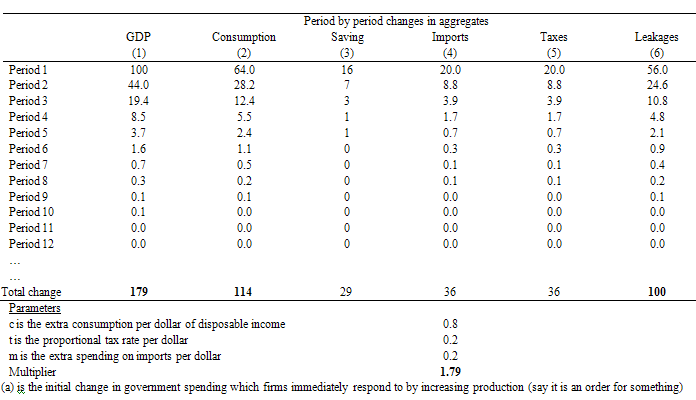
In the current example, the following spreadsheet table explains what is going on in terms of the economics.
So at the start of Period 1, the government increases spending by $100. The Table then traces out the changes that occur in the macroeconomic aggregates that follow this increase in spending (and “injection” of $100). The total change in real GDP (Column 1) will then tell us the multiplier value (although there is a simple formula that can compute it). The parameters which drive the individual flows are shown at the bottom of the table.
Note I have left out the full period adjustment – only showing up to Period 12. After that the adjustments are tiny until they peter out to zero.
Firms initially react to the $100 order from government at the beginning of the process of change. They increase output (assuming no change in inventories) and generate an extra $100 in income as a consequence which is the 100 change in GDP in Column [1].
The government taxes this income increase at 20 cents in the dollar (t = 0.20) and so disposable income only rises by $80 (Column 5).
There is a saying that one person’s income is another person’s expenditure and so the more the latter spends the more the former will receive and spend in turn – repeating the process.
Households spend 80 cents of every disposable dollar they receive which means that consumption rises by $64 in response to the rise in production/income. Households also save $16 of disposable income as a residual.
Imports also rise by $20 given that every dollar of GDP leads to a 20 cents increase imports (by assumption here) and this spending is lost from the spending stream in the next period.
So the initial rise in government spending has induced new consumption spending of $64. The workers who earned that income spend it and the production system responds.
But remember $20 was lost from the spending stream so the second period spending increase is $44. Firms react and generate and extra $44 to meet the increase in aggregate demand.
And so the process continues with each period seeing a smaller and smaller induced spending effect (via consumption) because the leakages are draining the spending that gets recycled into increased production.
Eventually the process stops and income reaches its new “equilibrium” level in response to the step-increase of $100 in government spending. Note I haven’t show the total process in the Table and the final totals are the actual final totals.
If you check the total change in leakages (S + T + M) in Column (6) you see they equal $100 which matches the initial injection of government spending. The rule is that the multiplier process ends when the sum of the change in leakages matches the initial injection which started the process off.
You can also see that the initial injection of government spending ($100) stimulates an eventual rise in GDP of $179 (hence the multiplier of 1.79) and consumption has risen by 114, Saving by 29 and Imports by 36.
In this case the change in the fiscal position would be (100-36) = $64 which has allowed private saving to rise. The implied current account deficit (with X fixed) would have increased a bit. A full model would introduce exchange rate effects. In this case, the exchange rate would likely fall a little (under the assumption of no change in autonomous X) which would stimulate X and reduce M a bit which would “crowd in” further income growth.
Further, inasmuch some imported inflation occurred (a tiny amount if any) then real interest rates would fall and might further stimulate output via investment. These additional effects are possible but probably fairly small in magnitude.
In general, the multiplier is larger the smaller the leakages. So the lower is the import leakage per dollar and the lower the taxation rate the larger the multiplier and the
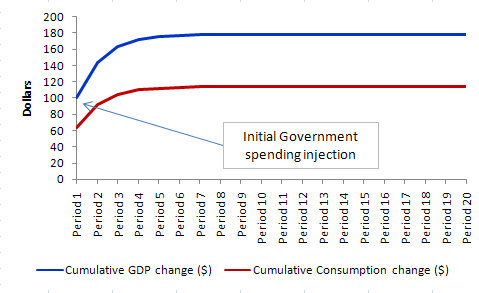
The following graph shows you the income and induced consumption adjustment path. The initial injection stimulates a lot of activity which then induces further consumption but in smaller and smaller amounts as the leakages impact in each period.
This type of approach also tells you that if the government was to cut taxes such that the households received the equivalent of $100 in extra disposable income the final multiplier would be lower because households will initially seek to save a proportion of the initial bonus. In other words, the first round injection would be less than the $100 and then the subsequent multiplier rounds would be smaller and the process would exhaust itself more quickly.
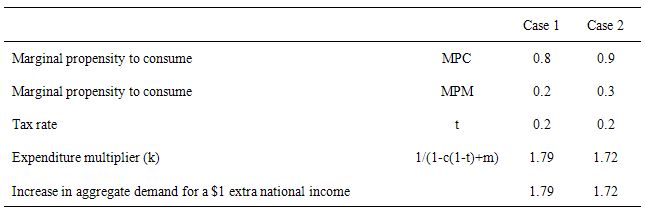
Now consider the two situations outlined in the question which are represented in the following Table.
You can see that when the MPC and the MPM both rise by 0.1 the expenditure multiplier falls from 1.79 (given starting values) to 1.72.
The reason? The rise in the MPM increases the drain on aggregate spending for every dollar of new national income by 10 cents. The rise in the MPC by 0.1 increases the induced consumption component by 10 per cent of every dollar of disposable income generated.
Given that the disposable income is less than total income (because of the positive tax rate), the increased import drain on spending is higher than the extra spending coming from the increased consumption and so the overall net impact of an extra dollar of national income falls.
The following blog post may be of further interest to you:
That is enough for today!
(c) Copyright 2021 William Mitchell. All Rights Reserved.
Dear Bill,
When I read something I’ve developed the habit of doing it very carefully, especially your stuff which occasionally are somehow rather esoteric. With this in mind allow me to pint point the following minor typos in your (as usually) excellent explanation.
1. “So if total disposable income is $80 (after taxation of 20 cents in the dollar is collected) then consumption (C) will be 0.80 times $80 which is $64 and saving will be the residual – $26 ? ($16).”
2. Y – c*(1-t)*Y + m*Y – ? (=) A
3. “Further, inasmuch some imported inflation occurred (a tiny amount if any) then real interest rates would rise ? (fall) and might further stimulate output via investment.”
4. “The reason? The fall ? (rise) in the MPM increases the drain on aggregate spending … “
One of my favorite debaters in your blog has accused me of nitpicking. If, you don’t share his characterization, would you consider me as a proof reader? 🙂
Respectfully,
Demetrios
Dear Demetrios Gizelis (at 2021/09/04 at 6:02 pm)
As a nitpicker you don’t rate, as a proof reader you excel.
Thanks very much for the latter duties (-:
Much appreciated.
bill
I don’t mean to be a nitpicker either but while having a morning coffee and reading through the answer to the quiz no. 3, I would add to the list, a typo no. 5:
In the last table, the second line should read “Marginal propensity to import” instead, I think…
Cheers,