A sovereign national government can run a balanced fiscal position over the economic cycle (peak to peak) as long as it accepts that after all the spending adjustments are exhausted that the private domestic balance will only be able to save overall if the external balance is in surplus.
Answer: True
The answer is True.
Note that this question begs the question as to how the economy might get into this situation that I have described using the sectoral balances framework. But whatever behavioural forces were at play, the sectoral balances all have to sum to zero. Once you understand that, then deduction leads to the correct answer.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
(1) GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X - M).
Expression (1) tells us that total income in the economy per period will be exactly equal to total spending from all sources of expenditure.
We also have to acknowledge that financial balances of the sectors are impacted by net government taxes (T) which includes all tax revenue minus total transfer and interest payments (the latter are not counted independently in the expenditure Expression (1)).
Further, as noted above the trade account is only one aspect of the financial flows between the domestic economy and the external sector. we have to include net external income flows (FNI).
Adding in the net external income flows (FNI) to Expression (2) for GDP we get the familiar gross national product or gross national income measure (GNP):
(2) GNP = C + I + G + (X - M) + FNI
To render this approach into the sectoral balances form, we subtract total net taxes (T) from both sides of Expression (3) to get:
(3) GNP - T = C + I + G + (X - M) + FNI - T
Now we can collect the terms by arranging them according to the three sectoral balances:
(4) (GNP - C - T) - I = (G - T) + (X - M + FNI)
The the terms in Expression (4) are relatively easy to understand now.
The term (GNP - C - T) represents total income less the amount consumed less the amount paid to government in taxes (taking into account transfers coming the other way). In other words, it represents private domestic saving.
The left-hand side of Equation (4), (GNP - C - T) - I, thus is the overall saving of the private domestic sector, which is distinct from total household saving denoted by the term (GNP - C - T).
In other words, the left-hand side of Equation (4) is the private domestic financial balance and if it is positive then the sector is spending less than its total income and if it is negative the sector is spending more than it total income.
The term (G - T) is the government financial balance and is in deficit if government spending (G) is greater than government tax revenue minus transfers (T), and in surplus if the balance is negative.
Finally, the other right-hand side term (X - M + FNI) is the external financial balance, commonly known as the current account balance (CAD). It is in surplus if positive and deficit if negative.
In English we could say that:
The private financial balance equals the sum of the government financial balance plus the current account balance.
We can re-write Expression (6) in this way to get the sectoral balances equation:
(5) (S - I) = (G - T) + CAB
which is interpreted as meaning that government sector deficits (G - T > 0) and current account surpluses (CAB > 0) generate national income and net financial assets for the private domestic sector.
Conversely, government surpluses (G - T < 0) and current account deficits (CAB < 0) reduce national income and undermine the capacity of the private domestic sector to add financial assets.
Expression (5) can also be written as:
(6) [(S - I) - CAB] = (G - T)
where the term on the left-hand side [(S - I) - CAB] is the non-government sector financial balance and is of equal and opposite sign to the government financial balance.
This is the familiar MMT statement that a government sector deficit (surplus) is equal dollar-for-dollar to the non-government sector surplus (deficit).
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)) plus net income transfers.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
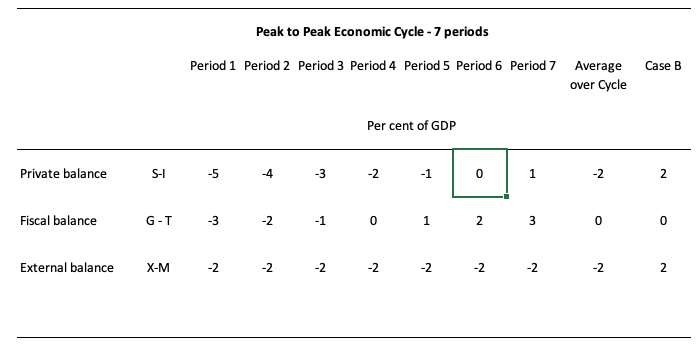
To help us answer the specific question posed, the following Table shows a stylised business cycle with some simplifications. The economy is running a fiscal surplus in the first three periods (but declining) and then increasing deficits.
Over the entire cycle the fiscal balance averages to zero. So the deficits are covered by fully offsetting surpluses over the cycle.
The simplification is the constant external deficit (that is, no cyclical sensitivity) of 2 per cent of GDP over the entire cycle.
You can then see what the private domestic balance is doing clearly. When the fiscal balance is in surplus, the private domestic balance is in deficit - househods and firms are spending more than they are earning overall.
The larger the fiscal surplus the larger the private deficit for a given external deficit.
As the fiscal position moves into deficit, the private domestic balance approaches balance and then finally in Period 6, the fiscal deficit is large enough to offset the demand-draining external deficit (2 per cent of GDP) and so the private domestic sector breaks even. By Period 7 the private domestic sector can save overall because the injection from the deficit is larger than the leakage from the external deficit.
The fiscal deficits underpin spending and allowing income growth to be sufficient to generate savings greater than investment in the private domestic sector.
On average over the cycle, under these conditions (balanced fiscal position) the private domestic deficit exactly equals the external deficit. As a result over the course of the economic cycle, the private domestic sector will become increasingly indebted if this situation persisted.
You can see in the Case B column, which shows average balances over some cycle that when the external position is in surplus, the private domestic sector can save overall even if the fiscal position is balanced at zero.
The following blog posts may be of further interest to you: