Assume that a nation is continuously running an external deficit of 2 per cent of GDP. If the private domestic sector successfully spends less than its overall income, then we would always find a public sector deficit.
Answer: True
The answer is True.
This question requires an understanding of the sectoral balances that can be derived from the National Accounts. But it also requires some understanding of the behavioural relationships within and between these sectors which generate the outcomes that are captured in the National Accounts and summarised by the sectoral balances.
Refreshing the balances (again) - we know that from an accounting sense, if the external sector overall is in deficit, then it is impossible for both the private domestic sector and government sector to run surpluses. One of those two has to also be in deficit to satisfy the accounting rules.
The important point is to understand what behaviour and economic adjustments drive these outcomes.
To refresh your memory the balances are derived as follows. The basic income-expenditure model in macroeconomics can be viewed in (at least) two ways: (a) from the perspective of the sources of spending; and (b) from the perspective of the uses of the income produced. Bringing these two perspectives (of the same thing) together generates the sectoral balances.
From the sources perspective we write:
(1) GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
which says that total national income (GDP) is the sum of total final consumption spending (C), total private investment (I), total government spending (G) and net exports (X - M).
Expression (1) tells us that total income in the economy per period will be exactly equal to total spending from all sources of expenditure.
We also have to acknowledge that financial balances of the sectors are impacted by net government taxes (T) which includes all tax revenue minus total transfer and interest payments (the latter are not counted independently in the expenditure Expression (1)).
Further, as noted above the trade account is only one aspect of the financial flows between the domestic economy and the external sector. we have to include net external income flows (FNI).
Adding in the net external income flows (FNI) to Expression (2) for GDP we get the familiar gross national product or gross national income measure (GNP):
(2) GNP = C + I + G + (X - M) + FNI
To render this approach into the sectoral balances form, we subtract total net taxes (T) from both sides of Expression (3) to get:
(3) GNP - T = C + I + G + (X - M) + FNI - T
Now we can collect the terms by arranging them according to the three sectoral balances:
(4) (GNP - C - T) - I = (G - T) + (X - M + FNI)
The the terms in Expression (4) are relatively easy to understand now.
The term (GNP - C - T) represents total income less the amount consumed less the amount paid to government in taxes (taking into account transfers coming the other way). In other words, it represents private domestic saving.
The left-hand side of Equation (4), (GNP - C - T) - I, thus is the overall saving of the private domestic sector, which is distinct from total household saving denoted by the term (GNP - C - T).
In other words, the left-hand side of Equation (4) is the private domestic financial balance and if it is positive then the sector is spending less than its total income and if it is negative the sector is spending more than it total income.
The term (G - T) is the government financial balance and is in deficit if government spending (G) is greater than government tax revenue minus transfers (T), and in surplus if the balance is negative.
Finally, the other right-hand side term (X - M + FNI) is the external financial balance, commonly known as the current account balance (CAD). It is in surplus if positive and deficit if negative.
In English we could say that:
The private financial balance equals the sum of the government financial balance plus the current account balance.
We can re-write Expression (6) in this way to get the sectoral balances equation:
(5) (S - I) = (G - T) + CAD
which is interpreted as meaning that government sector deficits (G - T > 0) and current account surpluses (CAD > 0) generate national income and net financial assets for the private domestic sector.
Conversely, government surpluses (G - T < 0) and current account deficits (CAD < 0) reduce national income and undermine the capacity of the private domestic sector to add financial assets.
Expression (5) can also be written as:
(6) [(S - I) - CAD] = (G - T)
where the term on the left-hand side [(S - I) - CAD] is the non-government sector financial balance and is of equal and opposite sign to the government financial balance.
This is the familiar MMT statement that a government sector deficit (surplus) is equal dollar-for-dollar to the non-government sector surplus (deficit).
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)) plus net income transfers.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
So what economic behaviour might lead to the outcome specified in the question?
If the nation is running an external deficit it means that the contribution to aggregate demand from the external sector is negative - that is net drain of spending - dragging output down. The reference to the specific 2 per cent of GDP figure was to place doubt in your mind. In fact, it doesn't matter how large or small the external deficit is for this question.
Assume, now that the private domestic sector (households and firms) seeks to increase its saving ratio and is successful in doing so. Consistent with this aspiration, households may cut back on consumption spending and save more out of disposable income. The immediate impact is that aggregate demand will fall and inventories will start to increase beyond the desired level of the firms.
The firms will soon react to the increased inventory holding costs and will start to cut back production. How quickly this happens depends on a number of factors including the pace and magnitude of the initial demand contraction. But if the households persist in trying to save more and consumption continues to lag, then soon enough the economy starts to contract - output, employment and income all fall.
The initial contraction in consumption multiplies through the expenditure system as workers who are laid off also lose income and their spending declines. This leads to further contractions.
The declining income leads to a number of consequences. Net exports improve as imports fall (less income) but the question clearly assumes that the external sector remains in deficit. Total saving actually starts to decline as income falls as does induced consumption.
So the initial discretionary decline in consumption is supplemented by the induced consumption falls driven by the multiplier process.
The decline in income then stifles firms' investment plans - they become pessimistic of the chances of realising the output derived from augmented capacity and so aggregate demand plunges further. Both these effects push the private domestic balance further towards and eventually into surplus
With the economy in decline, tax revenue falls and welfare payments rise which push the public fiscal balance towards and eventually into deficit via the automatic stabilisers.
If the private sector persists in trying to increase its saving ratio then the contracting income will clearly push the fiscal outcome into deficit.
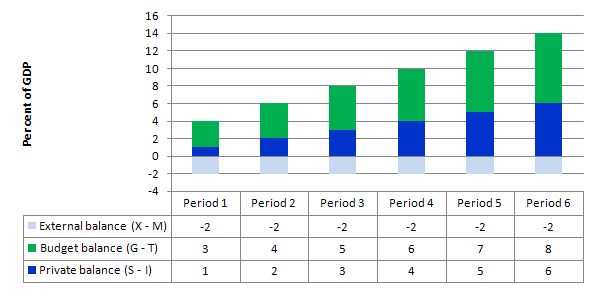
So if there is an external deficit and the private domestic sector saves (a surplus) then there will always be a fiscal deficit. The higher the private saving, the larger the deficit.
The following Graph and related Table shows you the sectoral balances written as (G-T) = (S-I) - (X-M) and how the fiscal deficit rises as the private domestic saving rises.
The following blogs may be of further interest to you: