Over a given economic cycle (peak to peak), if a nation's external sector is on average balanced and the government surplus of tax revenue over its spending is, on average, equal to 1 per cent of GDP, then the private domestic sector's spending-income balance will on average be in
Answer: Deficit of 1 per cent of GDP
The answer is Deficit of 1 per cent of GDP.
This is a question about sectoral balances. Skip the derivation if you are familiar with the framework.
First, you need to understand the basic relationship between the sectoral flows and the balances that are derived from them. The flows are derived from the National Accounting relationship between aggregate spending and income. So:
(1) Y = C + I + G + (X - M)
where Y is GDP (income), C is consumption spending, I is investment spending, G is government spending, X is exports and M is imports (so X - M = net exports).
Another perspective on the national income accounting is to note that households can use total income (Y) for the following uses:
(2) Y = C + S + T
where S is total saving and T is total taxation (the other variables are as previously defined).
You than then bring the two perspectives together (because they are both just "views" of Y) to write:
(3) C + S + T = Y = C + I + G + (X - M)
You can then drop the C (common on both sides) and you get:
(4) S + T = I + G + (X - M)
Then you can convert this into the familiar sectoral balances accounting relations which allow us to understand the influence of fiscal policy over private sector indebtedness.
So we can re-arrange Equation (4) to get the accounting identity for the three sectoral balances - private domestic, government fiscal balance and external:
(S - I) = (G - T) + (X - M)
The sectoral balances equation says that total private savings (S) minus private investment (I) has to equal the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)), where net exports represent the net savings of non-residents.
Another way of saying this is that total private savings (S) is equal to private investment (I) plus the public deficit (spending, G minus taxes, T) plus net exports (exports (X) minus imports (M)), where net exports represent the net savings of non-residents.
All these relationships (equations) hold as a matter of accounting and not matters of opinion.
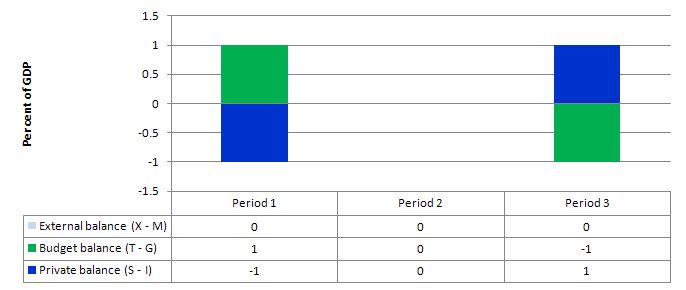
Consider the following graph which shows three situations where the external sector is in balance.
Period 1, is the case in point with the fiscal balance in surplus (T - G = 1) and the private balance is in deficit (S - I = -1). With the external balance equal to 0, the general rule that the government surplus (deficit) equals the non-government deficit (surplus) applies to the government and the private domestic sector. In other words, the private domestic sector must be spending ore than it is earning (a deficit).
In Period 3, the fiscal balance is in deficit (T - G = -1) and this provides some demand stimulus in the absence of any impact from the external sector, which allows the private domestic sector to save (S - I = 1).
Period 2, the fiscal balance is in balance (T - G = 0) and so the private domestic sector must also be in balance (spending equals its earning).
The movements in income associated with the spending and revenue patterns will ensure these balances arise. The problem is that if the private domestic sector desires to save overall then this outcome will be unstable and would lead to changes in the other balances as national income changed in response to the decline in private spending.
So under the conditions specified in the question, the private domestic sector cannot save. The government would be undermining any desire to save by not providing the fiscal stimulus necessary to increase national output and income so that private households/firms could save.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information: