 Which economy would deliver the largest national income bonus for a given discretionary expansion in government spending.
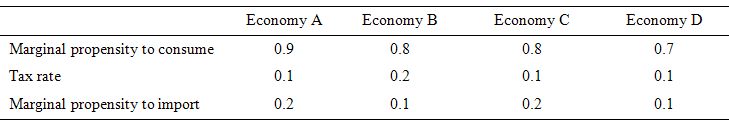
Which economy would deliver the largest national income bonus for a given discretionary expansion in government spending.Consider the following table which describes four different economies in terms of the behavioural parameters relating to the leakages to aggregate demand. Assume that in all four economies, there is idle capacity, the central bank holds all interest rates constant, inflation is constant and there is no changes in international competitiveness.
 Which economy would deliver the largest national income bonus for a given discretionary expansion in government spending.
Which economy would deliver the largest national income bonus for a given discretionary expansion in government spending.
Answer: Economy A
The answer is Economy A.
This question requires you to understand the impact of the different leakages (drains) to aggregate demand that arise from household saving, government taxation and import expenditure.
These leakages combine to determine the spending multiplier.
Students begin to learn about the expenditure multiplier in a very simple model without government or external sector. It sets them up immediately to disregard the crucial relationship between government and non-government sector that really drives the dynamics of the monetary system.
In the text book that Randy Wray and I are currently working on the government/non-government relationship is introduced at the beginning of the learning process to ensure students understand the importance of net positions etc.
So I don't think it is too hard to explain the expenditure multiplier with government spending, taxes and imports introduced from the start.
The clue is to first of all realise that aggregate demand drives output with generates incomes (via payments to the productive inputs). I won't go into controversies here about whether the productive inputs are rewarded fairly or whether surplus value is expropriated etc. That is a separate and not unimportant discussion but not germane here to understand the accounting and the dynamics.
Accordingly, what is spent will generate income in that period which is available for use. The uses are further consumption; paying taxes and/or buying imports. We consider imports as a separate category (even though they reflect consumption, investment and government spending decisions) because they constitute spending which does not recycle back into the production process. They are thus considered to be "leakages" from the expenditure system.
So if for every dollar produced and paid out as income, if the economy imports around 20 cents in the dollar, then only 80 cents is available within the system for spending in subsequent periods excluding taxation considerations.
However there are two other "leakages" which arise from domestic sources - saving and taxation. Take taxation first. When income is produced, the households end up with less than they are paid out in gross terms because the government levies a tax. So the income concept available for subsequent spending is called disposable income (Yd).
To keep it simple, imagine a proportional tax of 20 cents in the dollar is levied, so if $100 of income is generated, $20 goes to taxation and Yd is $80 (what is left). So taxation (T) is a "leakage" from the expenditure system in the same way as imports are.
Finally consider saving. Consumers make decisions to spend a proportion of their disposable income. The amount of each dollar they spent at the margin (that is, how much of every extra dollar to they consume) is called the marginal propensity to consume. If that is 0.80 then they spent 80 cents in every dollar of disposable income.
So if total disposable income is $80 (after taxation of 20 cents in the dollar is collected) then consumption (C) will be 0.80 times $80 which is $64 and saving will be the residual - $26. Saving (S) is also a "leakage" from the expenditure system.
It is easy to see that for every $100 produced, the income that is generated and distributed results in $64 in consumption and $36 in leakages which do not cycle back into spending.
For income to remain at $100 in the next period the $36 has to be made up by what economists call "injections" which in these sorts of models comprise the sum of investment (I), government spending (G) and exports (X). The injections are seen as coming from "outside" the output-income generating process (they are called exogenous or autonomous expenditure variables).
Investment is dependent on expectations of future revenue and costs of borrowing. Government spending is clearly a reflection of policy choices available to government. Exports are determined by world incomes and real exchange rates etc.
For GDP to be stable injections have to equal leakages (this can be converted into growth terms to the same effect). The national accounting statements that we have discussed previous such that the government deficit (surplus) equals $-for-$ the non-government surplus (deficit) and those that decompose the non-government sector in the external and private domestic sectors is derived from these relationships.
So imagine there is a certain level of income being produced - its value is immaterial. Imagine that the central bank sees no inflation risk and so interest rates are stable as are exchange rates and domestic wage levels (these simplifications are to to eliminate unnecessary complexity).
The question then is: what would happen if government increased spending by, say, $100? This is the terrain of the multiplier. If aggregate demand increases drive higher output and income increases then the question is by how much?
The spending multiplier is defined as the change in real income that results from a dollar change in exogenous aggregate demand (so one of G, I or X). We could complicate this by having autonomous consumption as well but the principle is not altered.
The spending multiplier is the extra spending that would occur when an autonomous expenditure source changes. So we ask the question: What would be the change in income if I or G or X changed by $1?
To derive the multiplier we need to write out the aggregate demand model and substitute the behavioural parameters into the model.
Aggregate demand (and income)
Y = C + I + G + X - M
Taxes
T = t*Y.
The little t is the marginal tax rate which in this case is the proportional rate. Note here taxes are taken out of total income (Y) which then defines disposable income.
The * sign denotes multiplication. You can do this example in a spreadsheet if you like.
Yd = (1-t)*Y
Consumption and Saving
We define the consumption relationship at the most simple level as a proportional relationship to disposable income (Yd).
C = c*Yd
where little c is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) or the fraction of every dollar of disposable income consumed.
So using the Yd relationship we can write consumption as:
C = c*(1-t)*Y
Imports
Imports (M) are considered proportional to total income (Y):
M= m*Y
where little m is the marginal propensity to import which is the increase in imports for every real GDP dollar produced.
Multiplier
To derive the multiplier formula we can assemble the aggregate demand relationship with its individual behavioural components as follows:
Y = C + I + G + X - M
Y = c*(1-t)*Y + I + G + X - m*Y
Now, re-arrange the equation to collect the Y terms on the left-hand side:
Y - c*(1-t)*Y + m*Y = I + G + X
You can see the exogenous injections to aggregate demand (those not reliant on national income) are on the right-hand side and all the components of expenditure that rely on national income are collected on the left-hand side.
We simplify this as follows:
Y(1 - c*(1-t)*Y + m) = I + G + X
So the relationship between changes in Y and changes in the exogenous spending components is:
Y = [1/(1 - c*(1-t)*Y + m)]*(I + G + X)
The term in [] brackets on the right-hand side is the multiplier because it shows how much a given change in (I + G + X) multiply to national income Y.
We could write this as:
Y = k*(I + G + X)
where
k = [1/(1 - c*(1-t)*Y + m)]
Or using other symbols:
k = 1/(1 - MPC x (1-t) + MPM)
So the higher is the MPC the lower is the tax rate (t) and the lower is the MPM the higher is the multiplier. That makes sense because taxes and imports drain spending from the income generating system. So as income responds positively to an autonomous injection, the smaller are the drains via taxation and imports and the higher the induced consumption - the higher is the second round spending effect which then continues to generate further income increases.
We can then apply this knowledge to the four economies in the Table. The bottom row of the Table provide the solution to the multiplier for the given parameters.
We interpret the data as follows. If government spending increased by $1, then the total change in national income in Economy A would be $2.56, in Economy B $2.17, in Economy C $2.08, and in Economy D $2.13.
The question obviously requires you to think about the different impacts of varying the drains on aggregate demand. The drains are not all equal.
For example, a given change in the marginal propensity to import has a greater impact than a given change in the marginal propensity to consume as you can see by comparing Economy C to Economy D. This is because imports come out of pre-tax income whereas the consumption decision comes out of disposable income.
A rise in the marginal propensity to consume of 0.1 will more than offset the draining impact of an equal rise in the tax rate because the decline in saving is greater than the rise in taxes.
You can construct all sorts of different scenarios to understand the impacts. To give you an idea of the different compositions of aggregate demand and the different leakages and injections the following Table assumes national income is 100 and then solves the model for each economy given the parameters.
I could clearly make the model more complex but the results would not be very different. Some will suggest the model is overly simplistic because it is a "fixed price" model and assumes supply will just meet any new nominal spending. That is true by construction and is a reasonable description of the state of play at present.
There is no inflation threat at present due to the vast quantities of idle resources that can be brought into production should there be a demand for their services.
Some might argue the external sector is too simplistic and that the terms of trade (real exchange rate) should be included in the export and import relationships. In a complex model that is true but in the context of this model the likely changes would just reinforce the results I derive. There is no loss of insight by holding the terms of trade constant.
Some might argue that the interest rate should be modelled and I reply why? The implicit assumption is that the central bank sets the interest rate and it is currently low in most nations and has been for some years. With no real inflation threat, the short-term rates will remain low for some time yet.
As to long rates (and the rising fiscal deficit) - show me where the significant rises in fiscal deficits (for a sovereign nation) are driving up rates. They have actually been falling as a consequence of very strong demand for public debt issues (almost insatiable) by bond markets and the quantitative easing efforts of the large central banks.
For an EMU nation, long-rates are within the control of the ECB as has been demonstrated once it started buying government bonds in the secondary markets. So leaving monetary policy implicit and fixed in this model doesn't lose any insight or "fix" the results in my favour.
You may wish to read the following blogs for more information:
That is enough for today!